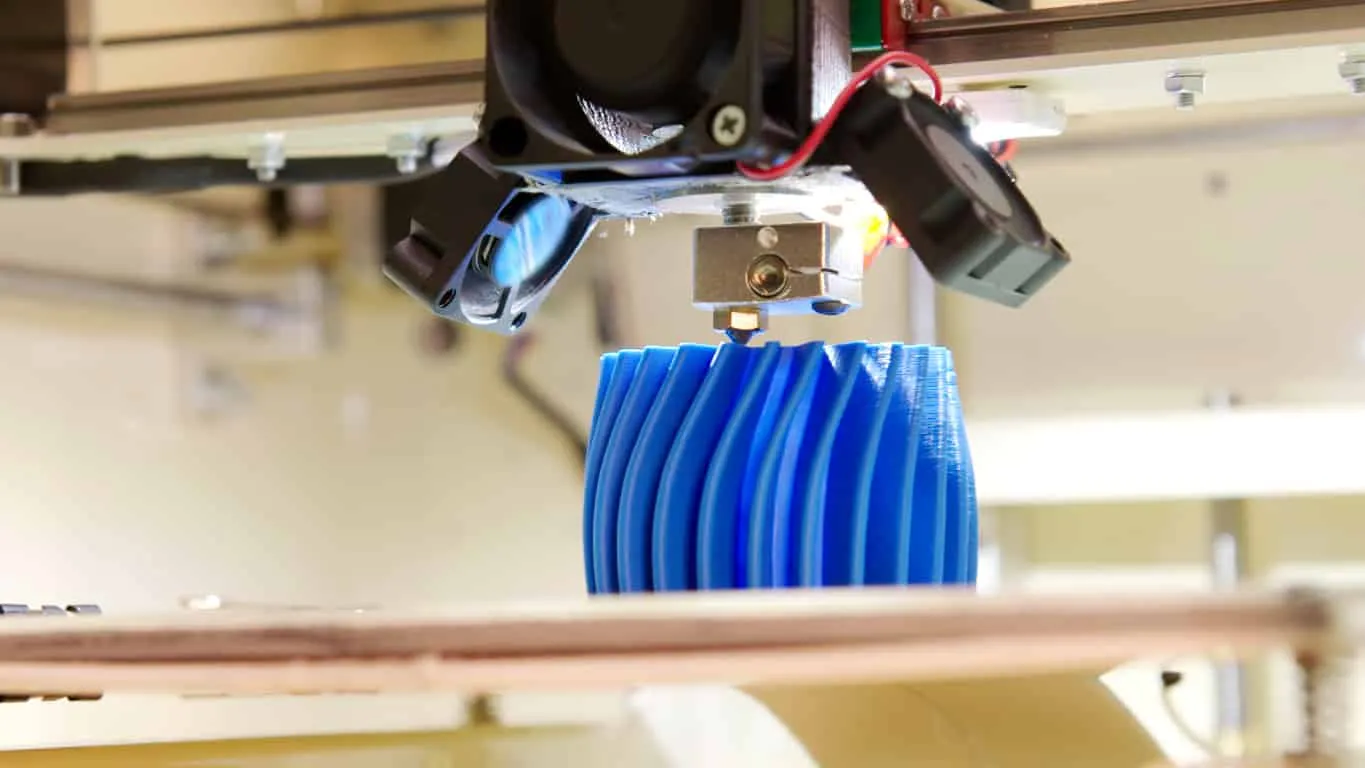
3D Printing Service
3DEXPERIENCE Make Online 3D Printing Service | Compare quotes from dozens of manufacturers.
SECURE PAYMENTS
Via payment card or purchase order
PROTECTED IP
Your data is confidential and secure with us. Use your own Non Disclosure Agreement
INSTANT QUOTE
For 3D Printing and CNC Machining, get quote in few seconds.
Discover SOLIDWORKS 3DEXPERIENCE for Makers
3D printing service with 3DEXPERIENCE Make
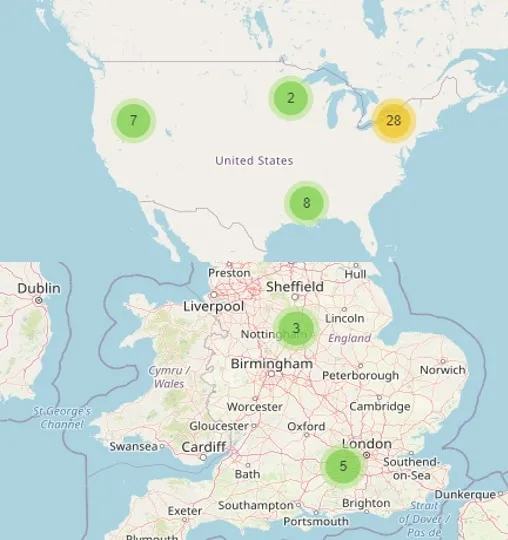
3DEXPERIENCE Make is an On-Demand Manufacturing platform, which connects designers or engineers with industrial 3D Printing service providers. Our service providers are mostly based in North America (the United States and Canada) and Europe (United Kingdom, France, Netherlands, Germany, etc.). 3D Printing service is today mostly used for Mockup or Prototyping (technical or presentation), but some of our partners can help you on small series, or even large series.
Thanks to our powerful algorithm, you can get a quote in seconds for your 3D Printing project from dozens of 3D Printing service providers.
Our 3D Printing service is handling projects in various industries such as Aerospace & Defense, Business Services, Construction, Consumer goods & retail, Energy & Materials, High-Tech, Home & Lifestyle, Industrial Equipment, Life Sciences & Healthcare, Marine & offshore, or Transportation & Mobility.
Our network of 3D Printing service providers offers hundreds of materials for your project, Plastic (PA12, ABS, PLA, PET, etc.), Metal (Stainless steel, 316, Aluminum, Titane, etc.), Ceramic, Wax, Sand or Composite (PA Glass, PA aluminum, ABS Carbon fiber, etc.).
Our online 3D printing services
Discover How 3DEXPERIENCE Marketplaces Boost Your Design to Manufacturing Process
You’re in good company. Thousands of leading companies from all industries use our solutions.
Our network of 3D Printing Services
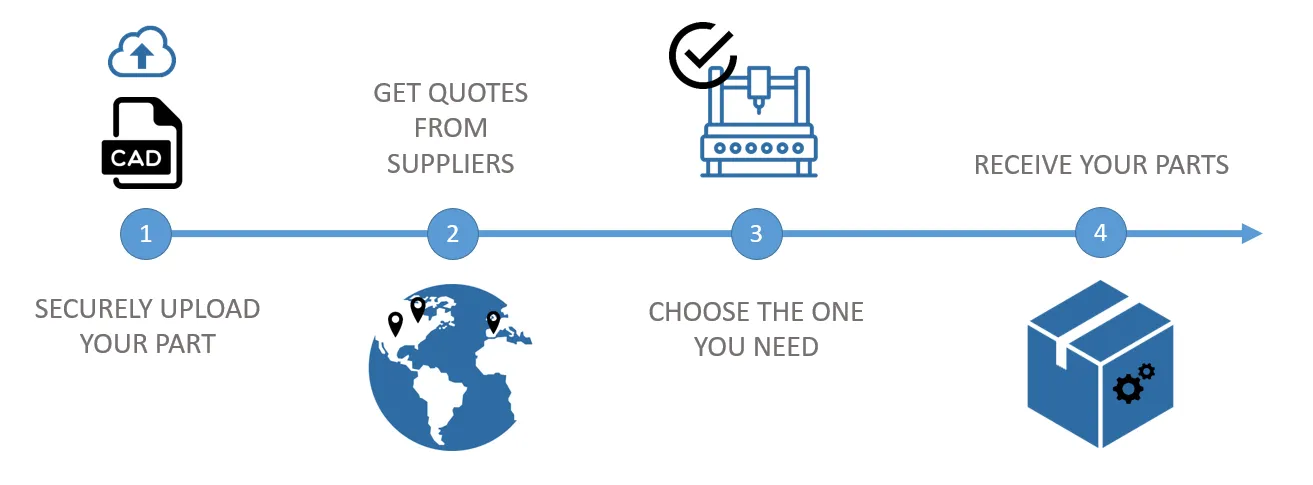
Online 3D Printing service: how does it work?
Materials of our 3D Printing Service Providers
Plastic
ABS, PLA, PET, TPU, ASA, PEI, PC, UV Curvable, PA, PP, etc.
Metal
Aluminium, 316/316L, Steel, Stainless Steel, Tool Steel, Nickel, Titanium...
Wax
Wax support, UV Curvable, etc...
Composite
PA Glass, PA Aluminium, Plastic Kevlar, ABS Carbon Fiber, etc...
Features to help you
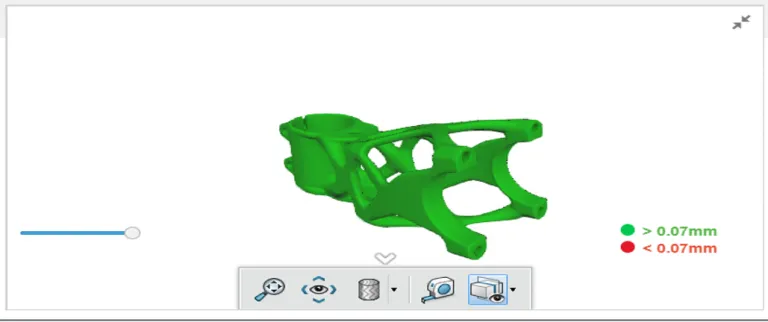
Check & repair or Geometry check is a feature that helps you to understand Geometry issue of your part and could repair it live and online.
Check & Repair
Check & repair or Geometry check is a feature that helps you to detect geometry issue on your part and repair it online and live.
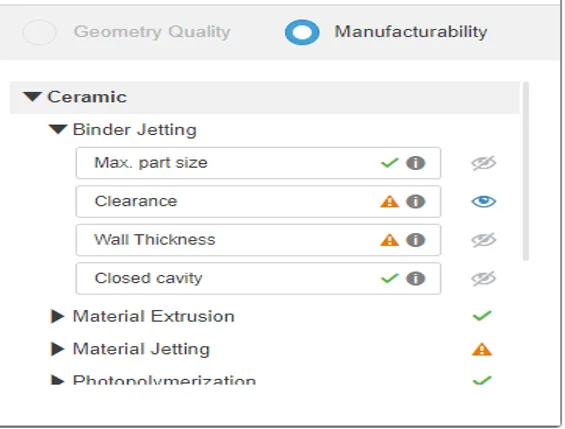
Manufacturability Check
This feature is available only for 3D Printing service. It helps you check the manufacturability of your part, depending on the materials and the process.
Instant quote engine
Receive in seconds several quotes thanks to our instant quote engine.
What is 3D printing?
3D Printing technology, also known as Additive Manufacturing (AM), refers to processes used to generate a 3D object. The machine forms layers of material successively under a computer-controlled program to create a physical object. Each layer generates a set of computer-controlled instructions thanks to the 3D File usually sliced into several layers. Both 3D printing and additive manufacturing reflect that the technologies share the theme of sequential-layer material addition or joining throughout a 3D work. Manufacturers generally categorized 3D printing technologies into two groups: direct and indirect 3D printing. The main difference lies in the fact that the design is directly made from 3D printing (direct) or 3D printing was used to create your model (indirect).
The objects manufactured through 3D printing processes can be of almost any shape or geometry. They are typically produced using digital model data from a 3D model or another electronic data source such as a StereoLithography (STL) file, one of the most common file types that 3D printers can read.
The term 3D printing originally referred to a process that deposited a binder material onto a powder bed with inkjet printer heads layer by layer. More recently, the term 3D printing represents a wider variety of additive manufacturing techniques in the popular vernacular. The additive manufacturing name remains more famous for its broader sense and longer existence for professionals. There are other terms, such as desktop manufacturing, rapid manufacturing, direct digital manufacturing, and rapid prototyping.
3D Printing its invention and usage for 3D Printing services
In the 1980s, Japanese, French, and American researchers invented additive manufacturing. In 1984, Chuck Hull of 3D Systems Corporation coined the very first patent of 3D Printing. Hull defined the 3D printing process as a system for generating three-dimensional objects by creating a cross-sectional pattern of the object to form it. His invention consists of a stereolithography fabrication system, adding layers by curing photopolymers with ultraviolet light lasers. Stereolithography is still one well-known 3D printing manufacturing technique known as SLA.
Yet, most 3D Printing services, especially hobbyists and consumer-oriented products, use Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), also known as material extrusion or the proprietary Stratasys denomination’s Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). In 1989 by S. Scott Crump patented FRM just before launching the Stratasys company with his wife, Lisa Crump.
Metal 3D printing only became available in the 1990s with the invention of laser melting and sintering techniques. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Selective Laser Melting (SLM) are often grouped under the umbrella term Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
ISO/ASTM52900-15 defines seven categories of Additive Manufacturing (AM) processes material extrusion, vat photopolymerization, powder bed fusion, material jetting, binder jetting, sheet lamination, and directed energy deposition.
Our Manufacturing service uses the same classification, with simplified terms, to avoid complexity and confusion:
Material extrusion
Photopolymerization
Powder bed fusion
Material jetting
Binder jetting
Sheet lamination
Directed energy deposition
The possibilities with 3D Printing are boundless and encompass numerous industries from plastics and metals up to organic materials and food. A broad range of materials is used in 3D Printing. Each one carefully corresponds to the technical requirements of the end product and is usually fitted for only a restrictive set of additive manufacturing technologies.
3D Printing and materials, what can do a 3D printing service?
In order to illustrate the vast potential for 3D Printing, it is necessary to get a basic understanding of the most popular materials. Let’s begin with sintered powdered metal used for printing the injection molds used in classic manufacturing like casting, injection molding, and carbon fiber lay-up. Stainless steel, bronze, steel, gold, nickel steel, aluminum, and titanium are just a few of the suitable metals for 3D printing. These metals are particularly well suited for prototyping, jewelry, and tailored objects. Furthermore, Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium, delivers a promising outlook for the medical implant industry. Its superelasticity and ability to change shapes are two features that astonish the scientific community.
A significantly broad spectrum of plastics offers an extensive field of possibilities for 3D Printing. Far from an exhaustive list, some possible plastics include acrylics, polyamides, ABS plastic, assorted polyurethanes, epoxy resins, nylon, and PEBA 2301. These plastics offer a plethora of conceivable objects such as prototypes, gear systems, ornaments, or educational modeling. Additionally, wax can be an essential element for design verification, functional testing, fine feature details, smooth surface finish, and tooling mold.
Carbon fiber and composites are cutting-edge materials that offer a fast way of producing an object that is as strong or stronger than metal. The bicycle and aeronautics industries most commonly employ them. Graphene, an allotrope of carbon, is the most robust material ever tested. It has the potential to create new technologies, thanks, in part, to its efficient heat and electrical conductivity and its near-transparent appearance.
Some more unusual materials encompass stem cells, paper, concrete, food, and yarn. As difficult as it may be to imagine, the 3D Printing of stem cells is a showstopper in 3D Printing technology. It would make it possible to print tissues, organs, or bones implanting into a patient.
3D Printing of paper offers a full-color spectrum for designers that want to produce a realistic 3D model before advancing a product onto final engineering. Concrete is currently used for housing portions and even entire homes in China. The food sector is testing and employing for 3D Printing chocolate, pizza, and cake decorations. Also, the wide range of materials makes it possible to produce yarn with 3D Printing.
3D Printing Subprocesses
3D Printing and materials, what can do a 3D printing service?
In order to illustrate the vast potential for 3D Printing, it is necessary to get a basic understanding of the most popular materials. Let’s begin with sintered powdered metal used for printing the injection molds used in classic manufacturing like casting, injection molding, and carbon fiber lay-up. Stainless steel, bronze, steel, gold, nickel steel, aluminum, and titanium are just a few of the suitable metals for 3D printing. These metals are particularly well suited for prototyping, jewelry, and tailored objects. Furthermore, Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium, delivers a promising outlook for the medical implant industry. Its superelasticity and ability to change shapes are two features that astonish the scientific community.
A significantly broad spectrum of plastics offers an extensive field of possibilities for 3D Printing. Far from an exhaustive list, some possible plastics include acrylics, polyamides, ABS plastic, assorted polyurethanes, epoxy resins, nylon, and PEBA 2301. These plastics offer a plethora of conceivable objects such as prototypes, gear systems, ornaments, or educational modeling. Additionally, wax can be an essential element for design verification, functional testing, fine feature details, smooth surface finish, and tooling mold.
Carbon fiber and composites are cutting-edge materials that offer a fast way of producing an object that is as strong or stronger than metal. The bicycle and aeronautics industries most commonly employ them. Graphene, an allotrope of carbon, is the most robust material ever tested. It has the potential to create new technologies, thanks, in part, to its efficient heat and electrical conductivity and its near-transparent appearance.
Some more unusual materials encompass stem cells, paper, concrete, food, and yarn. As difficult as it may be to imagine, the 3D Printing of stem cells is a showstopper in 3D Printing technology. It would make it possible to print tissues, organs, or bones implanting into a patient.
3D Printing of paper offers a full-color spectrum for designers that want to produce a realistic 3D model before advancing a product onto final engineering. Concrete is currently used for housing portions and even entire homes in China. The food sector is testing and employing for 3D Printing chocolate, pizza, and cake decorations. Also, the wide range of materials makes it possible to produce yarn with 3D Printing.
Questions People ask about 3D Printing service
What is a 3D Printing Service?
Additive manufacturing—commonly called 3D Printing—is an ideal solution for creating concept models, manufacturing tooling, functional prototypes, and even end-use parts in many cases. Online 3D printing services are used by design firms and part manufacturers for making prototypes and molds. 3D printers are sophisticated machines that use advanced technology adhering to very high-quality standards. 3D printers must also be able to print large objects efficiently, which can impact the 3D printing service cost. In terms of hardware, a standard professional 3D printer can cost over $100,000.
Commercial 3D printers come in a wide variety of sizes. Many commercial 3D printers are similar in size to large office copy machines. These printers generally weigh between 30 to 150 kilograms. Generally speaking, the higher the printer's resolution, accuracy, and speed, the bigger the printer will be. Therefore, 3D printers that print production-grade parts are larger. Some of these 3D printers can weigh upwards of 1,000 kilograms.
3D printing services use technologies such as FDM, SLS, SLA, and PolyJet. The specific technology used depends on the manufacturer's history and experience. Part designers and engineers need to keep in mind build volume when it comes to online 3D printing services. Build volume limits the largest size at which a given part can be printed at one time. Build size also depends on the specific 3D printer model as well as the manufacturer's experience level.
From a 3D printing materials perspective, each manufacturer offers its own variety of proprietary 3D printing materials. Materials are an essential consideration, and designers must make sure a given manufacturer can print their desired material. Examples of common materials include thermoplastics (ABS, PC, ULTEM), photopolymers, SLA, and SLS.
3D printing software programs are often complex and thrive on flexibility and customization. Each manufacturer typically specializes in a few different software platforms. Resolution is an important concept in 3D Printing as it describes the minimum thickness of the build layer. Resolution requirements are specified for all professional 3D printing applications. Commercial 3D printers can achieve resolutions as low as 16 microns. Some commercial 3D printers can print layers only three microns thin at the high end.
There are many different applications for professional 3D Printing, such as concept modeling, which involves bringing early-stage ideas and concepts to life. Concept modeling is often used at design, engineering, and architecture firms for testing, proofing, and optimizing designs. One of the key benefits of 3D printers is their ability to make moving parts in different materials. This capability unlocks a door that allows designers and engineers to print fully functional prototypes for testing. Rapid prototyping enables increased productivity and helps identify errors early in the design process.
The 3D printing service process allows manufacturers to make casts and molds for tools, fixtures, and jigs within a matter of hours. These capabilities drastically reduce production times. Reducing costs and speeding up production means that manufacturers can use 3D printers to create end-use parts directly without tooling. Professional 3D printing services are often used in the defense, medical, aerospace, consumer goods, automotive, and architecture industries.
How Do I Select the Right 3D Printing Process for My Prints?
Each 3D printing service process has its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Some 3D printing processes will be a better fit for particular applications compared to others. In our experience, we've found it can be helpful to approach the 3D printing process selection based on material, use-case, or manufacturing capabilities.
Material-Based Selection
Materials used in 3D Printing typically include powder, filament, or resin. As such, plastics and metals are the two most common 3D printing material categories. However, it's worth noting that materials such as composites or ceramics can also be used.
Suppose designers and engineers have already decided what material to use in their prints for their prototype or part. In that case, the corresponding 3D printing process will often be chosen by default since certain technologies are best suited for specific materials.
Use-Case Driven Selection
If possible, engineers and designers should try to decide early on how important visual aesthetics is in their design compared to functionality. Knowing the answer to this question will help you decide which 3D printing service process is most suitable for your prototype or part. Generally speaking, the thermoplastic material is optimal for functional-oriented parts, whereas thermosets are better for aesthetic purposes.
When designing a prototype that will interact with other components, it's vital that you define your tolerance levels. The higher the dimensional accuracy requirements are for your part, the greater the 3D printing service cost will be.
Manufacturing Capabilities-Based Selection
If you've already completed the prints for your part, the particular capabilities of each additive manufacturing technology will play a primary role in the 3D printing service process selection. Dimensional accuracy is critical when determining the tolerances each process can satisfy, as well as the overall quality of the part. If your print requires very tight tolerances, you must select a 3D printing process that can achieve these tolerances and intricate features.
Why choose 3D printing?
You can use 3D printing for many reasons. The applications are now very diverse and all industries are using this technology.
Reduced cost for mock-ups, prototypes, customized products and small series
3D printing is a so-called additive technology, it works by adding material, unlike machining or cutting. It is, therefore, less material-consuming and more cost-effective.
This is especially true since 3D printing is often a process that even for complex parts has a simpler supply chain, as is the case with the proliferation of fablabs.
However, you must keep in mind that 3D printing offers almost no economy of scale.
So, based on these advantages, 3D printing remains the perfect cost-effective process for producing small quantities of even complex parts.
Speed
Even if the time to manufacture a part remains several hours, 3D printing offers unparalleled advantages in terms of production time, thanks to its agility and the light supply chain.
These time savings help accelerate Product Life Management by improving:
—The mock-up and prototyping phases. By offering speed and agility, R&D departments can test prototypes faster and in greater quantity in the first phases of the product’s life.
—Pre-production. 3D printing can be more economical for certain types of products or for relatively small numbers of small series.
—Production series. As seen above, 3D printing is not (yet) optimal for mass production. However, the process is extremely efficient for creating molds for plastic injection molding, again saving valuable time.
—The life of the product. If the company wishes to create personalized products or small series, 3D printing will take all its place. The creation of advertising tools is also easier with 3D printing services.
—Spare parts. 3D printing services can, in some cases, be very useful to produce spare parts. This allows them to be manufactured on demand, thus avoiding the need to store/produce parts that may never be used.
In short, at every stage of a product’s life cycle, 3D printing can play a major role in accelerating, facilitating, or saving money, and with a better Go to Market.
Greater design freedom
3D printing technology gives designers greater freedom than more traditional CNC machining or cutting techniques. The spectrum of possible geometric shapes is infinitely wider and easier to realize.
Dassault Systèmes offers Generative Design solutions that allow you to modify your designs to free them from the traditional constraints of machining or injection, and to make parts that are optimized in terms of cost and resistance, to be printed.
Another frequently used form is weaving, which offers the possibility to reinforce parts while saving weight and material.
How much does your 3D Printing service cost?
Our service is an On-Demand Manufacturing marketplace. Designers and engineers could connect through a platform with a network of industrial manufacturers specialized in 3D printing. Some of these 3D printing services work with us to provide you with instant quotes based on your 3D file. These pricing engines are made with algorithms that are based on past orders and their exact costs. So you can get multiple quotes from our network in the U.S. or Europe in seconds.
This way, there are no surprises when you place your request, you know immediately the exact price of our service. However, in rare cases, your part may be difficult to estimate (depending of the shape, the size or the volume), and the price displayed may be revised by the 3D printing service. Please be aware that until they confirm the purchase price, the price may be subject to change. During this time, your credit card will not be charged.
The website is free to use. Simply create an account on our 3DEXPERIENCE Make site, then upload your CAD file, and you can enjoy our instant quote or ask for quote manually to our 3D Printing service partner. This process can be accomplished in SOLIDWORKS and CATIA, and you can find bridges to 3DEXPERIENCE Make in Draftsight and eDrawings.
When designing a new project or a new part, our platform can be used to optimize your part. All you have to do is reload your project each time you make a change. In SOLIDWORKS and CATIA, you can see the price of your part as you modify your design.
Our instant pricing engines have been worked on by our 3D printing service partners to get the right price for their current constraints.
If you want to find out how to evaluate the price of a 3D printed part by yourself, I suggest you read this article, how to evaluate the price of a 3D printed part.
How to evaluate the cost of 3D Printing?
The question is quite broad, generally, there are several criteria that come into play to estimate the cost of a 3D part.
The exact process used
3D printing is the generic term (the name used in the industry is additive). It is then divided into several sub-categories: photopolymerization, powder bed fusion, material extrusion (FDM), binder jetting, material jetting…
Each process has advantages and disadvantages depending on the characteristics of your part.
The material used
There are many possible materials, various types of plastic, metal, wax, etc. Each of these materials will also influence the cost, as they have a different price per kilo.
Materials have different properties, so it is necessary to make the right compromise between the price and your technical needs.
The number of parts produced
3D printing is often perceived as a technology with a fixed unit price, meaning that the price has little variation according to the number of parts produced. While this is true for the production phase, there can be significant economies of scale if your parts require significant post-production time. Nevertheless, keep in mind that 3D printing is not (yet) the most suitable solution for mass production.
The type of printer of your 3D Printing service
There are all kinds of printers on the market, more or less precise, more or less reliable. In the 3D printing sector, even in the professional sector, it is rare to get the print right the first time, and the higher the quality of the printer, the less likely it is to fail.
Shipping costs and taxes
If you use an on-demand 3D printing service like 3DEXPERIENCE Make, you will have the choice of several manufacturers located in different regions. Obviously, you will have to add shipping costs to the final price and possibly custom taxes.
Finishes
Depending on your request, 3D printing may require more or less work in post-production. I advise you to discuss these costs with your 3D printing service provider and see how to reduce them.
The size of the part
3D printing does not appear to be suitable for very large parts. Most printers only measure a few tens of cm3. Thus, the larger your object, the fewer 3D printing services will be available, and the higher the price will be.
Complexity of the object
3D printing can offer very low costs for very complex objects compared to machining or cutting. However, some designs or CAD files may require more advanced printers or/and more post-production work.
3D printing service
3DEXPERIENCE Make offers to request several quotes at the same time, which allows you to make an informed choice easily and thus reduce your risks and budgets.
How can I reduced the cost of my 3D Printed part?
There are 9 costs associated with 3D printing, the 3D printing technology used, the material used, the number of parts produced, the type of printer, the shipping costs, the finishing touches, the size and complexity of the part and the manufacturer. Each of these points can be optimized to lower your quote.
You can read a full article on: how to reduce the cost of manufacturing your part or assembly.
I offer the 3 most important tips:
Choose standard parts
One of the easiest ways to reduce the cost of your part or assembly is simply to start with an existing standard part or to reduce drastically the number of custom parts in your assembly.
We have developed a tool that allows you to check if your part is similar or not to an existing standard part from our 60 million parts library: PartSupply Similarity. You can learn more about this app by watching this video.
Calculate the cost of your part often in the design phase
By regularly checking the price of your part on our 3DEXPERIENCE Make platform or through our add-in, SOLIDWORKS or CATIA will ensure that your design modifications do not impact the overall price of your project.
Optimize the part
There are different ways to optimize your part, it can be choosing the right material, reducing the volume of the part, or adding lattices in your structure.
How do you select your 3D Printing Service providers?
Dassault Systèmes, through its brands as CATIA, SOLIDWORKS, DELMIA … and its resellers, already has many years of experience in the manufacturing sector. We have selected our 3D printing services from them.
When external 3D printing services contact us, we verify their information with a dedicated and experienced team.
Our suppliers are only based in Europe or North America and are verified, industrial manufacturers. We don't accept individuals as service providers, even if they have strong expertise.
How do you guarantee the quality of the part?
Our network of manufacturers is only composed of industry professionals. Most of them have been customers of our brands like SOLIDWORKS or CATIA for years.
When you go through our platform, during the payment process, we secure your money until you validate the delivery of your order (or two weeks after the supplier has set the SHIPPED status). Thus, we help you to manage the dispute with the 3D printing service. The supplier will be paid only once the dispute is resolved.
Where Can I Learn More About 3D Printing?
At Dassault Systèmes, our 3DEXPERIENCE Make service provides you with an on-demand manufacturing platform which connects designers and engineers with industrial 3D Printing service providers. Our 3D Printing service providers are based in the United States, Canada, and Western Europe. We leverage our proprietary algorithm to get you a 3D printing quote from dozens of 3D printing service providers in seconds.
Discover our other manufacturing services
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds