SIMULIA High-Tech Solutions
Deliver compliant High-Tech systems quickly and to cost
Simulation for the High-Tech Industry
The High-Tech industry is one of the fastest-growing and most competitive sectors in the economy. Technological development's rapid pace means manufacturers must constantly innovate to remain competitive. Shorter design cycles, reduced development costs, and new ways of working are essential to building and maintaining a lead in the market.
Simulation enables engineers to analyze the performance of a device before constructing a prototype and to optimize it to meet design requirements and regulations. By shifting analysis left in the development cycle, engineers can identify potential issues and find their causes at the first stages of development, allowing them to be resolved quickly before costs spiral. Virtual testing can reduce or replace the need for physical tests, cutting reliance on expensive prototypes and accelerating development.
The SIMULIA brand of Dassault Systèmes offers a portfolio of simulation tools covering multiple physical disciplines. Simulation can be integrated into industry-standard electronics design automation (EDA) and computer-aided design (CAD) workflows, and other Dassault Systèmes tools on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform to enable unified modeling and simulation (MODSIM).
Key Benefits of High-Tech Solutions
Reduce Time-to-Market
Shorten development and gain a competitive edge
Cut Development Costs
Stay on budget by reducing design iterations and physical prototypes
Optimize Performance
Develop innovative products that meet and exceed requirements
Test Virtually
Accelerate analysis and compliance with virtual certification
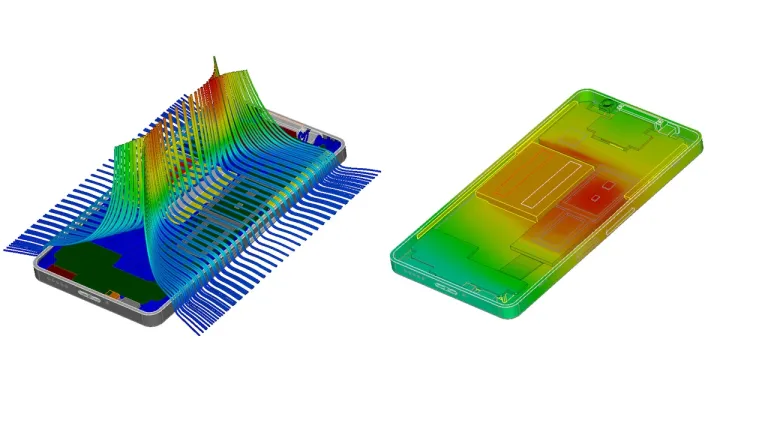
Electromagnetic Simulation
High-tech devices cover the entire electromagnetic spectrum, from static and DC up to millimeter wave and even photonics. The SIMULIA simulation portfolio includes industry-leading electromagnetic solvers for low-frequency and high-frequency applications, including specialist tools for applications such as PCBs and cables.
Structural Simulation
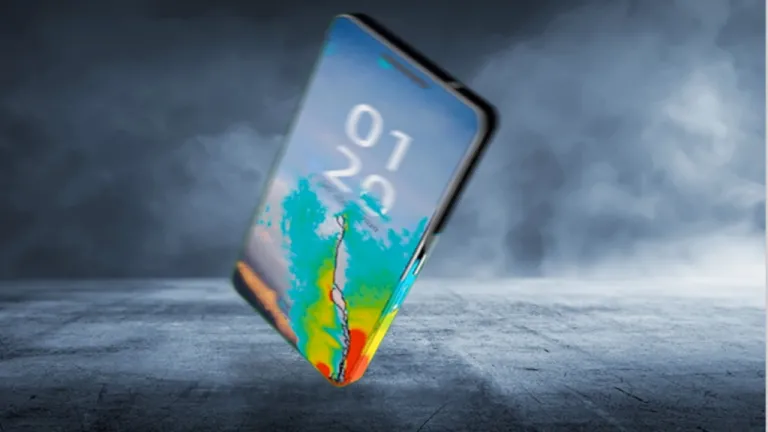
Structural simulation is required to analyze how devices will withstand the rigors of daily use such as drops, vibration and water-immersion. Simulation can replicate potential damage scenarios without the cost of constructing – and breaking – physical prototypes. Fatigue simulation also reveals how components such as connectors behave over many years with thousands of use cycles.
Electromechanical Simulation
Mechanical components are used as sensors, and to provide sound, vibration and haptic functionality. Electromechanical simulation can analyze of these components and optimize their performance. Links to vibro-acoustic simulation can also identify noise sources from vibrating components and resonances.
Thermal Simulation
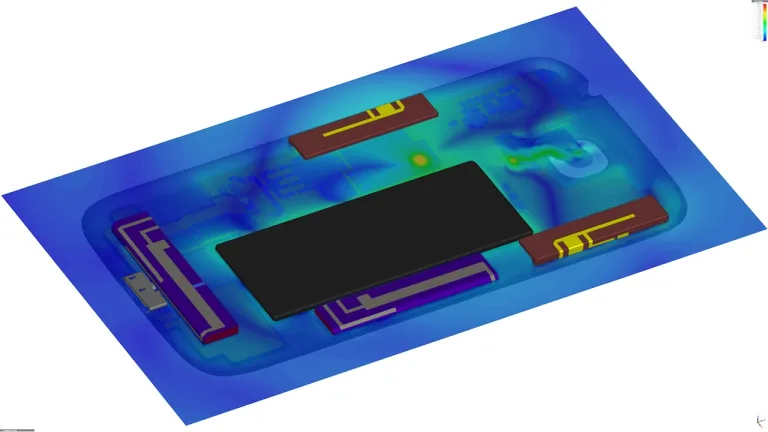
Electrical losses give rise to heat that can damage components. Managing heat inside devices can be challenging, especially for handheld devices with many components in close proximity and no scope for cooling fans. Coupled electromagnetic-thermal simulation can calculate how devices will heat up in use, including the effect of air flow, and the effectiveness of cooling systems such as heat sinks and fans.
Bio-Electromagnetics
Regulations limit the allowed exposure of the human body to electromagnetic radiation. Measurements such as specific absorption rate (SAR) are used to quantify exposure. Simulation can calculate SAR both inside standard test phantoms and realistic human body models under actual usage scenarios. Simulation reduces the risk of potential violations being discovered late in testing.
MODSIM for High-Tech
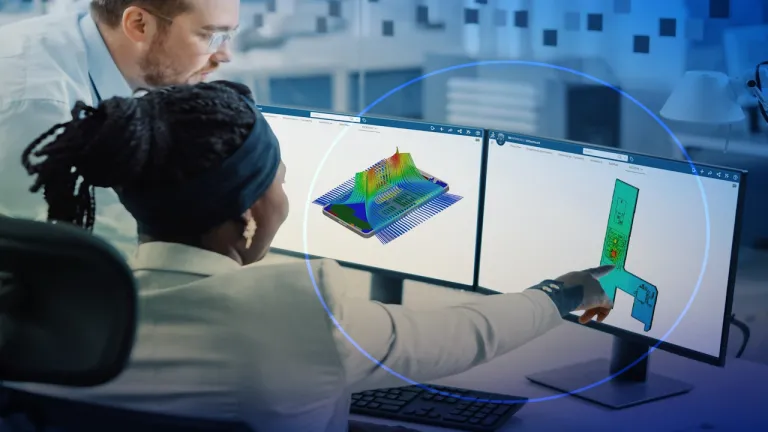
Traditionally, designers and analysts work in different departments and are relatively siloed. These leads to inefficiencies in exchanging information and means that problems are typically discovered late when fixing it is more expensive. Unified modeling and simulation (MODSIM) brings designers and analysts together, allowing them to easily exchange data, keep files up-to-date, and analyze the performance of a design at any stage in development.
Virtual Certification
In order to reduce the time and resource cost of getting products certified, regulators increasingly accept simulated test results alongside or instead of physical tests. Reliable simulation results can significantly reduce the number of physical tests required to get certification from bodies such as the FCC.
Electronics Design Automation Workflow Integration
Simulation can easily integrate into the standard industry electronics design automation (EDA) workflows used to design PCBs, packages and chips. Automatic rule checkers analyze layouts and highlight potential signal integrity, power integrity (SI/PI), and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) issues. Layouts can then be imported into 3D simulation to identify potential problems caused by complex interactions that other analysis methods miss.
Electronics Design Analysis
Increasing data rates and a trend toward miniaturization make electronic design more challenging. More channels and components must be integrated into an ever-shrinking area, which means more potential for crosstalk and other signal integrity and power integrity (SI/PI) effects. To reduce the error rate and the risk of interference, SI/PI and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) must be considered during layout.
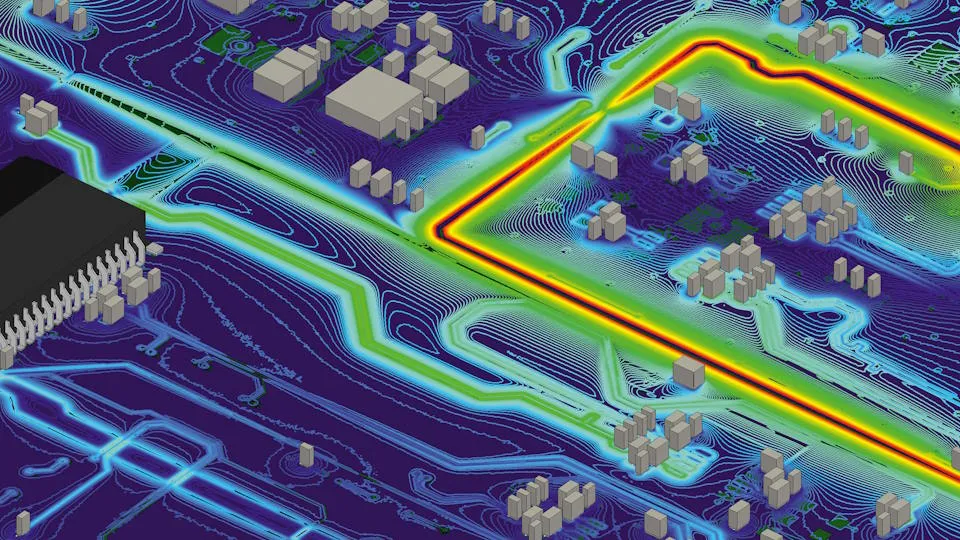

Electromagnetic compatibility
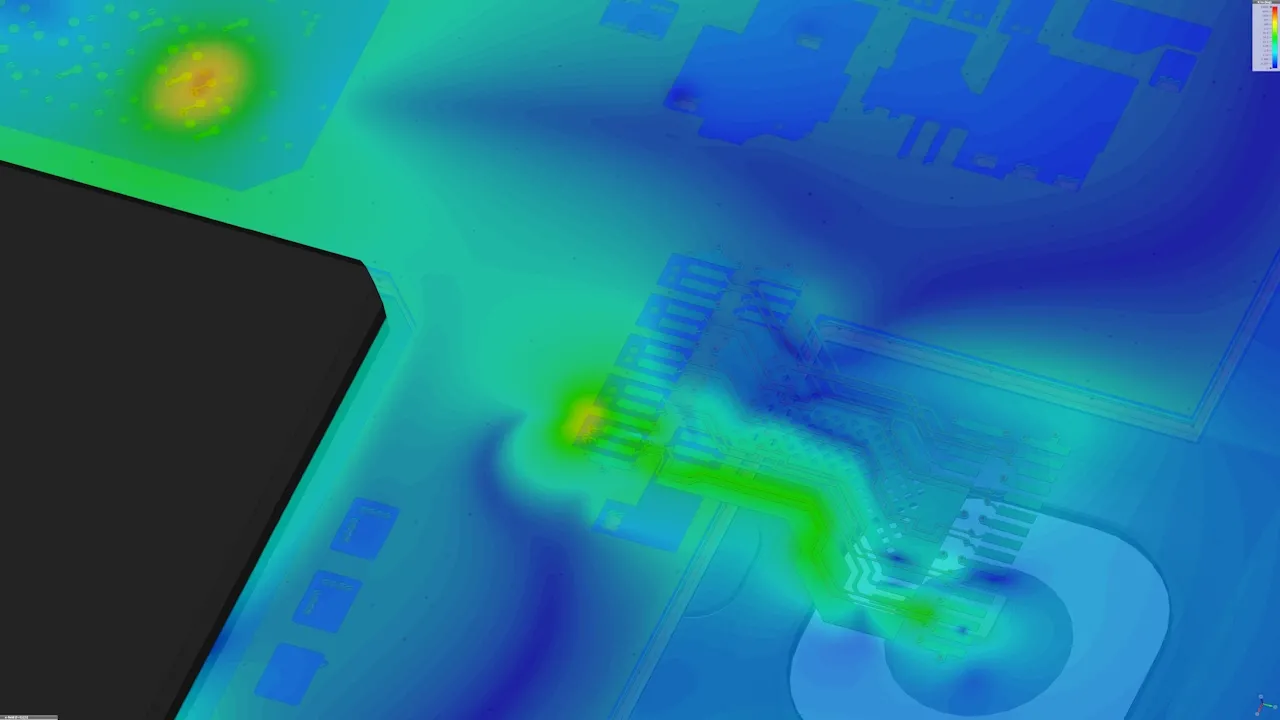

Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is the ability of a device to operate without causing interference to other systems, and while tolerating potential interference. EMC simulation can replicate EMC test scenarios with a virtual prototype, without the cost of constructing a physical prototype. This accelerates the analysis process and reduces the risk of problems being identified late and delaying the project.
Battery Engineering
Batteries are among the largest components in any device, and maximizing their capacity is crucial to increasing battery life and reducing size and weight. Simulation helps battery engineers to design robust, safe battery cells and to understand and control heat within the device. Potential dangerous scenarios such as short-circuit, impact and swelling can be safely tested on a virtual twin. BIOVIA Materials Studio also allows electrode and electrolyte chemistry to be analyzed.

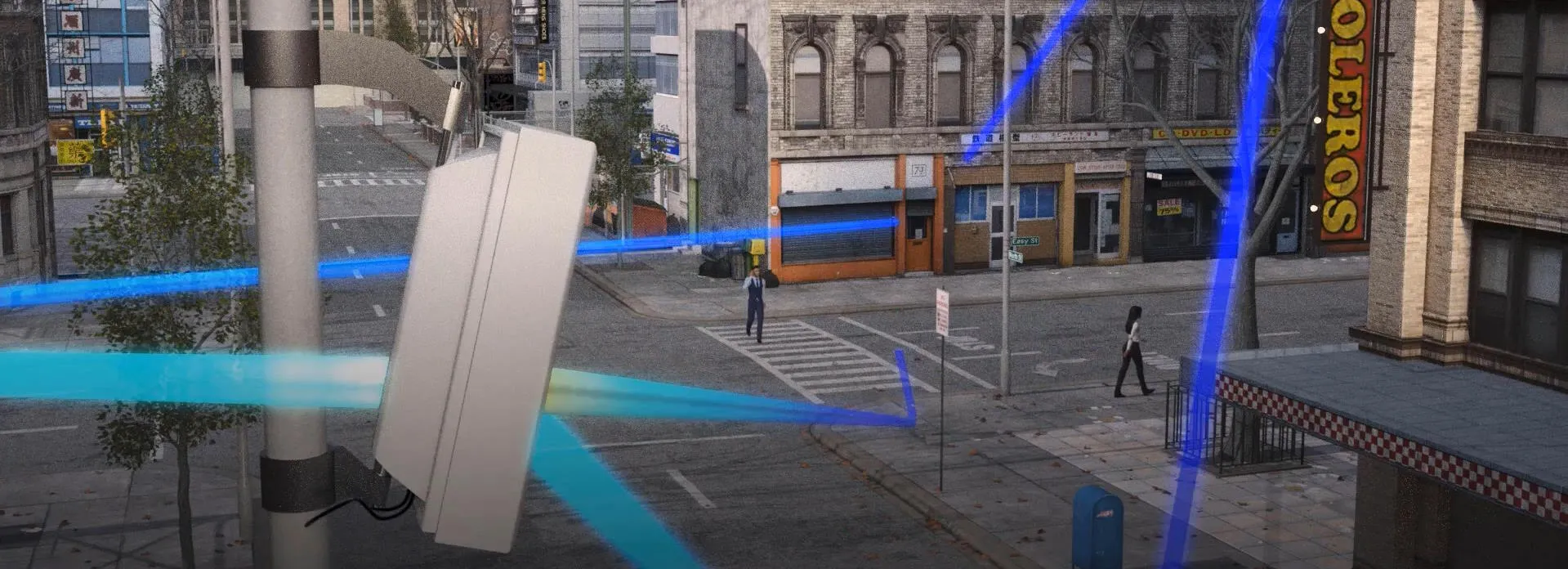
Communication Infrastructure Simulation
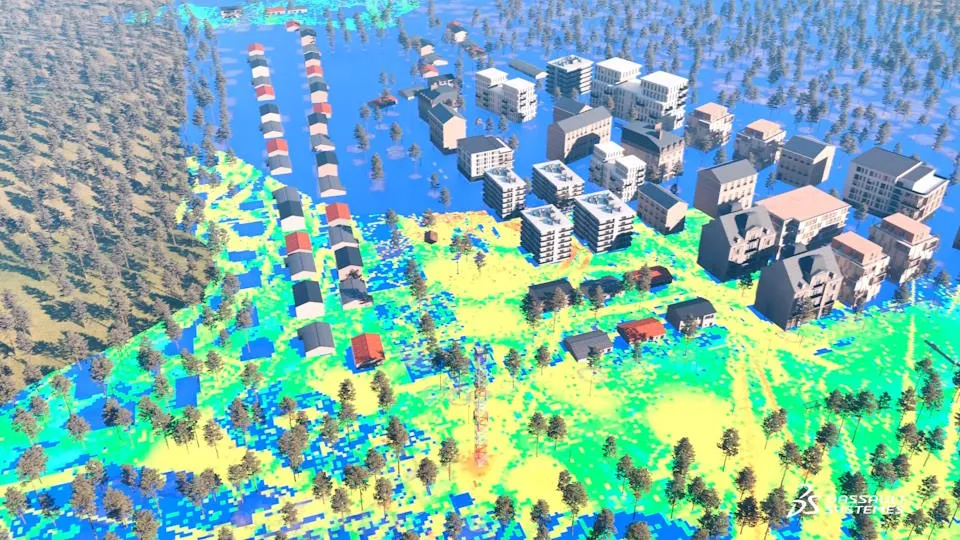

Both the public internet and private networks require a strong backbone. With so many wireless devices all operating in complex environments and competing for spectrum, ensuring reliable and high-speed data connections without interference can be a challenge. Simulation can be used to design infrastructure backend devices from routers to transmitter antennas, and to optimize their performance as part of a full system. EMC performance, signal and power integrity and thermal cooling can all be analyzed as part of an integrated workflow.
Simulation is enabling the 5G rollout and the development of upcoming 6G technology, giving device designs and systems engineers the ability to analyze system performance before constructing a physical prototype. Network coverage in complex physical environments such as city streets or smart factories can be mapped using simulation to identify zones of poor reception under different scenarios and to optimize wireless antenna placement.
Consumer Device Simulation
Consumer electronics represent one of the most important segments for the high tech industry. This is a highly competitive market, and customers are demanding devices that are not only faster and more efficient, but also smaller, lighter, cheaper and more stylish. Maintaining a competitive edge in this industry requires rapid development cycles in order to bring a product to market, while also minimizing risk of compliance test failures that lead to delays, costly redesigns and potentially even recalls.
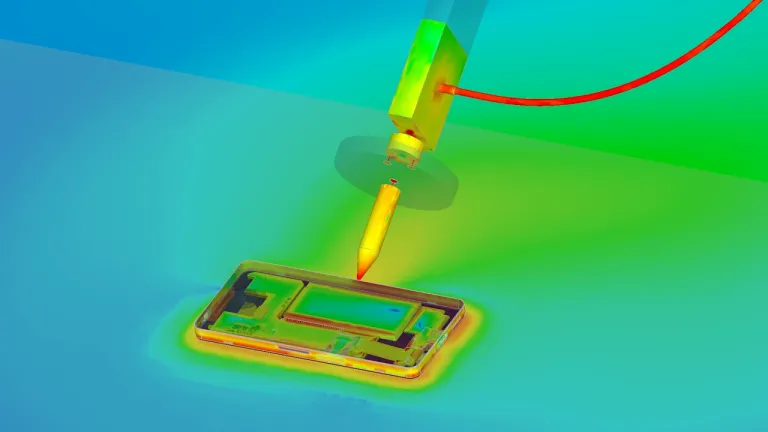
Simulation is used by leading manufacturers of consumer electronics devices, from smartphones and laptops to wearables and smart products, in order to replace time-consuming and expensive physical prototypes with virtual testing. Performance, EMC, cooling and durability can be analyzed on a virtual twin of the real device, revealing potential issues much earlier in the design process and allowing them to be resolved quickly. Products can be brought to market faster and cheaper, with increased confidence that they will meet the requirements of users in the real world.

Semiconductor Packaging
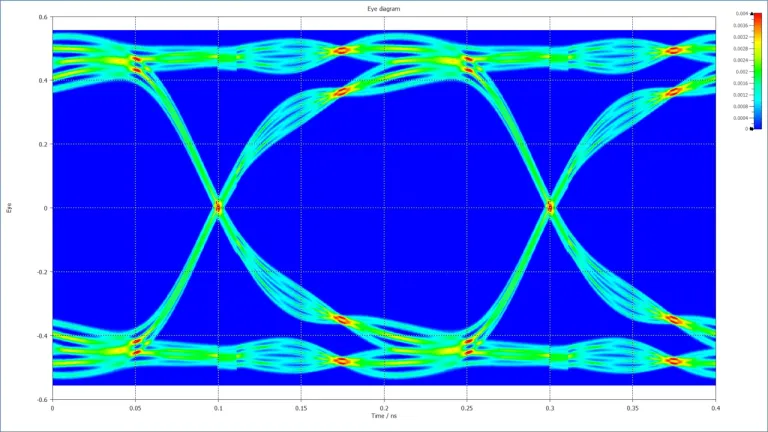
Integrated circuit (IC) chips are placed inside packages to protect them and allow them to be mounted onto printed circuit boards (PCBs). The package needs to be able to transmit signals from the data channels on the PCB, through contacts such as pins or ball-grid arrays (BGAs), and to the IC and back - all without causing interference or data loss.
Electronic engineers use simulation in the semiconductor packaging design process in order to model the propagation of currents through the socket and package and identify potential signal integrity (SI) and power integrity (PI) problems. Simulation can replicate standard electronic engineering tests such as time-domain reflectometry (TDR) and eye diagrams virtually, allowing engineers to find problems without having to construct a virtual prototype. Coupled electromagnetic-thermal simulation can also model cooling on the package, helping to optimize the placement of heat sinks and fans.
Thermal performance and electronics cooling
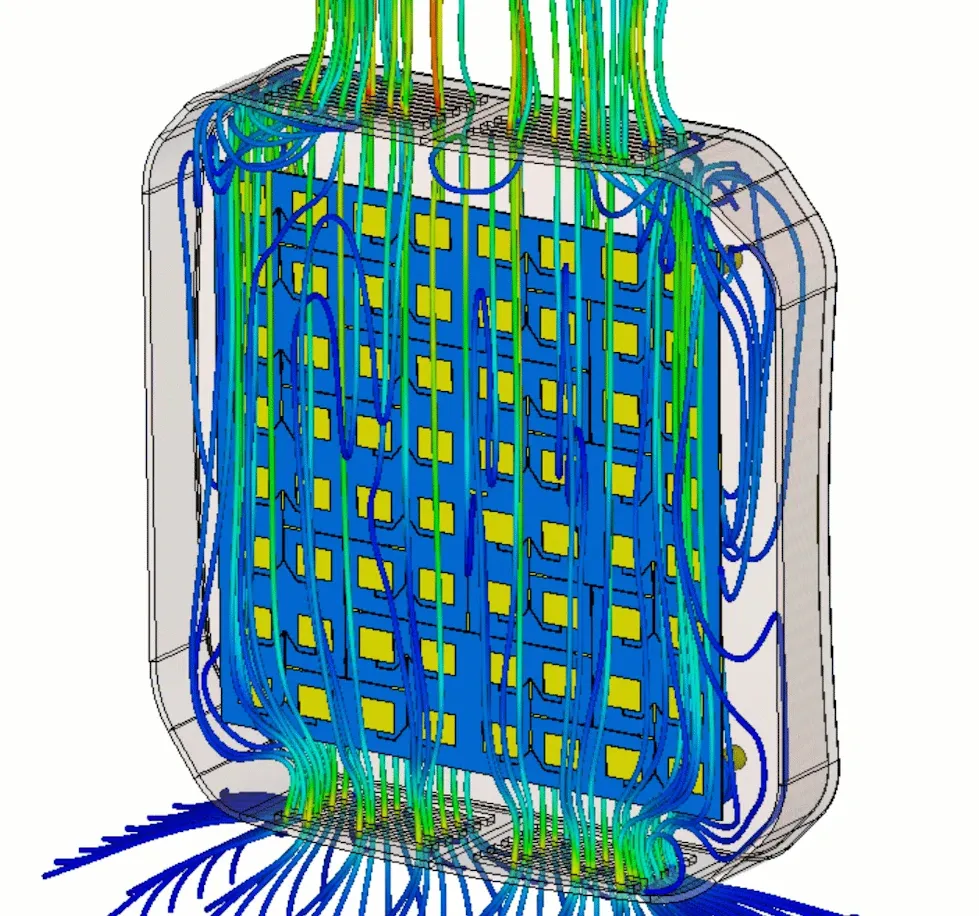
Miniaturization means that a lot of power is concentrated in very small areas, resulting in significant heat generation in components such as interconnects and batteries. Understanding where heat is produced and how it dissipates is a multidisciplinary problem combining electromagnetics, thermodynamics and fluids. Coupled multiphysics simulations help engineers to identify heat sources and design effective cooling systems.
SIMULIA Customers in High-Tech
SIMULIA Industry Solutions for High-Tech
High-tech enhances our modern and connected lives with always-on experiences. As capabilities and opportunities rise exponentially, high-tech companies must become ever more responsive to re-invent and sustain their leading edge while mastering complexity, quality and margin pressures. Dassault Systèmes' 3DEXPERIENCE platform empowers high-tech innovators to innovate faster, yet more sustainably.
Start your Journey
The world of High-Tech is changing. Discover how to stay a step ahead with SIMULIA.
Also Discover
Learn What SIMULIA Can Do for You
Speak with a SIMULIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right SIMULIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering