SLS ABS 3D Printing
You landed on the article about SLS ABS 3D printing
Introduction to SLS ABS 3D Printing
The selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing method creates objects from engineering files by sintering, a process that uses powder to make an object by heating it with a laser. SLS technology was developed in the mid-1980s and is currently at the forefront of rapid prototyping and production. ABS is the acronym for acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is one of the most common thermoplastic polymers, and is commonly used for a wide variety of products. It was patented in 1948 and commercially available for plastic molding in 1954.
What is ABS?
ABS, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, is one of the most common thermoplastic polymers injection molded part manufacturing. It is also used for 3D printing prototype development. It is an opaque thermoplastic and amorphous polymer. This means that it is a non-crystalline plastic that can be heated to its melting point, cooled and set, and then reheated without notable degradation. It is a relatively inexpensive material with a low melting point and good durability and strength.
ABS is light, dimensionally stable, and yields structurally sturdy products. It is a good choice for strong and sturdy plastics that are inexpensive and easy to manufacture. It has strong impact resistance and excellent acoustic and thermal insulation properties. ABS can be used in subsequent machining and painting operations. ABS is relatively harmless, with no known carcinogens, but it is typically unsuitable for medical implants.
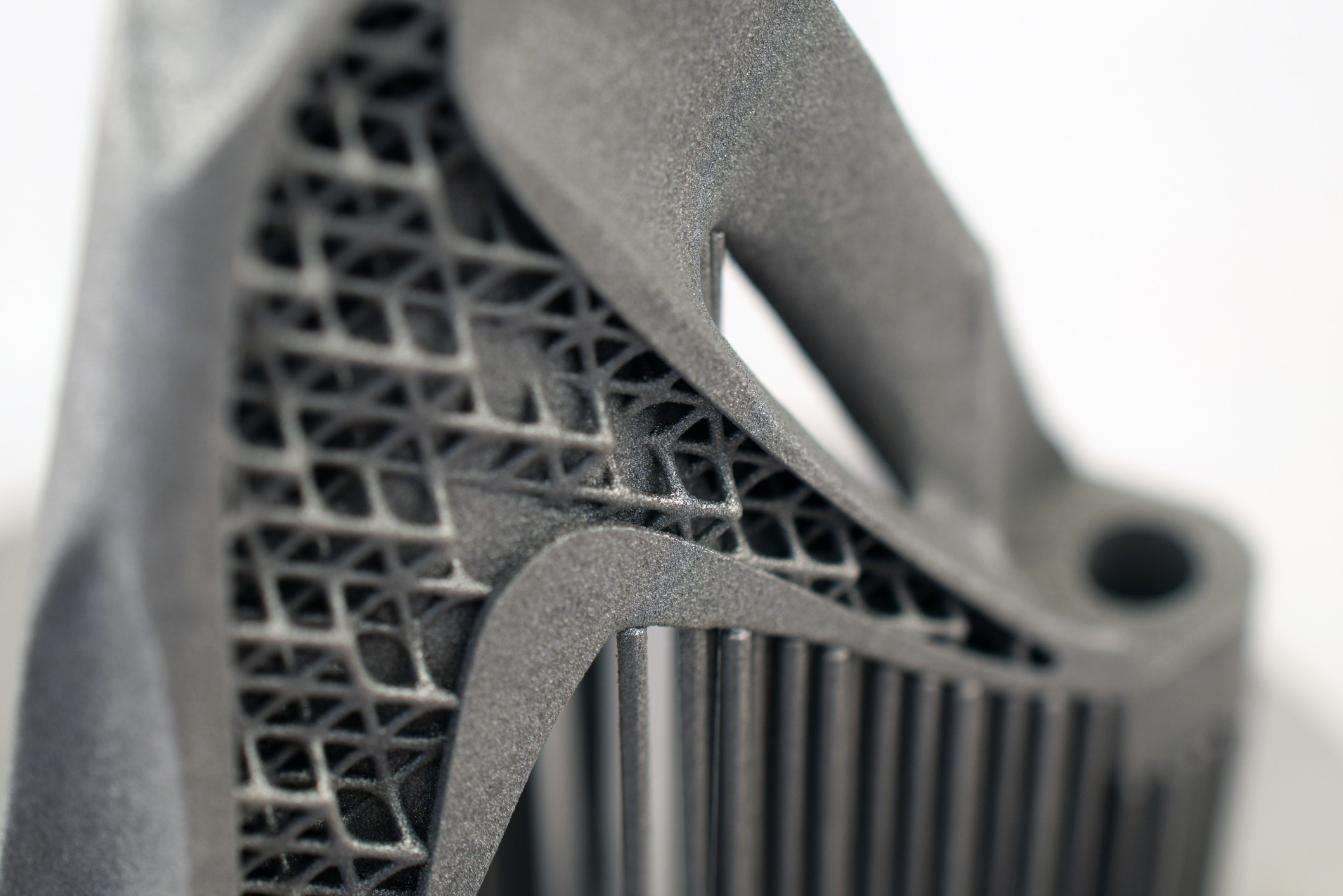
What is SLS 3-D Printing?
Selective laser sintering (SLS) uses a laser for the sintering process to heat the powder in a layer-by-layer process. The laser binds the particles and is controlled by two motorized mirrors at the top of the construction chamber. A powder bed surrounds the part as it is printed, which supports the part being printed. The bed also utilizes a roller system to spread thin layers of powder before the sintering process. A heater in the bed preheats the powder so the laser can melt and bond the polymer particles. The loose powder is removed upon completion, and the part is ready for painting, machining, etc. The unsintered powder can be used for the next production run, making SLS a zero-waste technology.
It is a popular additive manufacturing process due to its high productivity and low cost per part. The process has exceptional accuracy, including solid parts and complex geometries without structural support requirements. With mechanical properties similar to injection-molded products, SLS is the preferred process for functional prototyping and final end-use products. SLS printed parts have comparative strength to many metal parts while being much lighter and less expensive. Nylons, polymers, metals, ceramics, and various specialty materials are used in SLS printing, with Nylon, and PLA as some of the more common materials.
SLS ABS 3D Printing is incompatible - Use FDM ABS instead
The versatility for mass customization of complex geometries of SLS printing makes an excellent process for printing robust prototypes and production products.SLS ABS 3D printing is actually incompatible and we recommend using FDM with ABS for better result. It is used in a wide variety of commercial products in the R&D, architectural, medical, aerospace, automotive, and jewelry industries, as well as commercial products. These applications include protective housings, computer keyboard keys, printers, kitchen appliances, hardhats, plastic faceguards, architectural models, robotics, automotive components, window thermal barriers, F1 racing components, and toys.
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds
