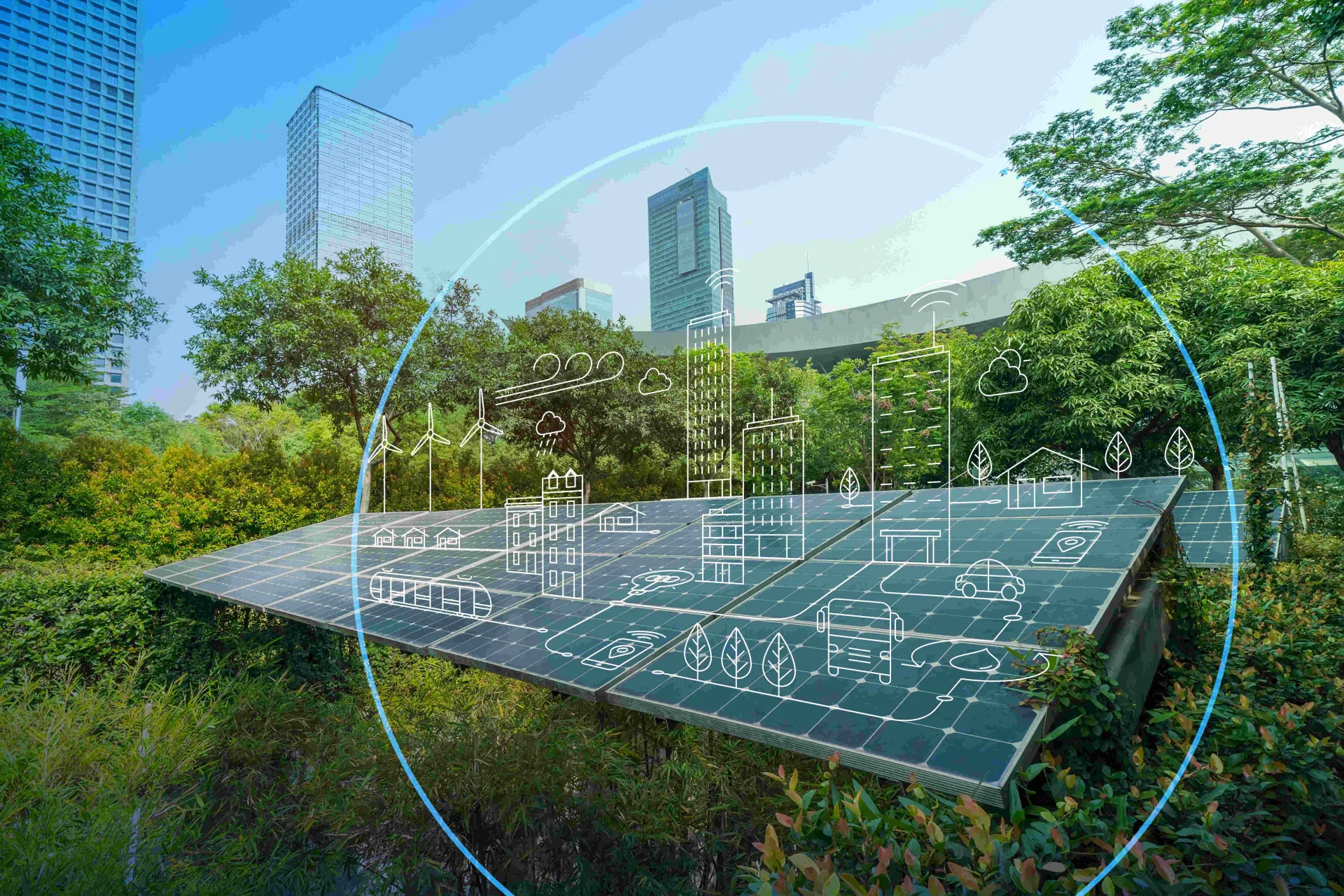
Sustainable Energy
Low-carbon energy generates substantially lower greenhouse gas emissions over their entire lifecycle.
What is Energy Use?
Energy use describes the amount and type of energy required by an organization to provide goods and services. With advanced digital tools and processes, efficient resource management and new (or existing) infrastructure optimization, organizations can make strategic decisions to alter their patterns of energy use and reduce their carbon footprint.
What Does It Mean for Your Business?
Reducing your energy use footprint doesn’t just mean smaller energy bills. Reducing your carbon footprint helps you stay ahead of regulatory requirements, and create a more resilient business that respects the environment. This not only appeals to today’s sustainability-conscious consumers but lays the groundwork for a meaningful zero carbon transition.
The Challenges of Changing Energy Use
Realizing effective low-carbon energy operations for your business can be a challenge. Firstly, it requires you to effectively measure and manage the different forms of energy you are currently using. Then, it means finding a way of changing existing operations for a more efficient use of energy from greener sources, alongside integrating new clean energy technologies and processes to modernize old infrastructures and implement new ones.
Benefits of Dassault Systèmes’ Technologies
Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE® platform provides a powerful suite of tools that can help understand and transform your organization’s energy production, use and infrastructure.
Phase out fossil fuel power generation
Model and simulate energy grids (neighborhood, city and region) to fully integrate and deploy an energy mix with intermittent energy production (solar, wind and hydro) and nuclear power.

Innovative and accessible energy production
Dare bold new energy production initiatives for different consumption patterns adapted to local needs for production, maintenance and end-of-life.
Energy storage
Create new flexible energy storage opportunities to safeguard the planet’s resources and respond to a fluctuating demand (smart grid, V2G, batteries).

Support de-growth of energy use
Measure and analyze your energy consumption, thanks to advanced digital tools, to consume less energy in every step of your approach.
Real-World Results, As Told by Our Customers
Read our case studies to see how Dassault Systèmes solutions can help you make the most out of sustainable energy solutions.
Solutions for Sustainable Energy Use
Innovation is key for building a path to sustainability, and those looking to make the transition can take advantage of several options:
| Solutions | Details |
| Electrification |
|
| Energy Storage |
|
| Energy Use |
|
Each solution contributes to sustainable energy use by promoting cleaner power sources, increasing flexibility, and reducing overall energy consumption.
Making a Positive Impact on Society
FAQ About Energy Use & Renewable Energy Sources
Related Content
Advancing Clean Energy Technologies
Shifting from fossil-based energy systems to sustainable and low-carbon alternatives has become, now more than ever, crucial. Clean energy technologies already exist.
The Power Plan for a Smooth Energy Transition
Backed by innovative solutions, extensive experience and concrete strategies to decarbonize global energy systems, we aim to energize your transition initiatives and catalyze sustainable change.
Biodiversity Through Circularity
With virtual twin-powered strategies, businesses can protect biodiversity while unlocking new revenue streams.
Decarbonization
Decarbonization aims at reducing emissions throughout the product and service’s life cycle and across the full value chain.