Video: VAT Photopolymerization
Discover in video how the 3D Printing process VAT Photopolymerization works with 3DEXPERIENCE Make, the on-demand manufacturing, by Dassault Systèmes and his partner Sculpteo.
Video: What is Photopolymerization?
Hello, we’re here at Sculpteo, a 3DEXPERIENCE Make Marketplace partner. Today’s topic is photopolymerization.
Photopolymerization is a 3D printing process that involves using a heat source to solidify liquid photosensitive resin. This process occurs in 3D printing techniques such as stereolithography and DLP and 3D color printing via Polyjet and Multijet.
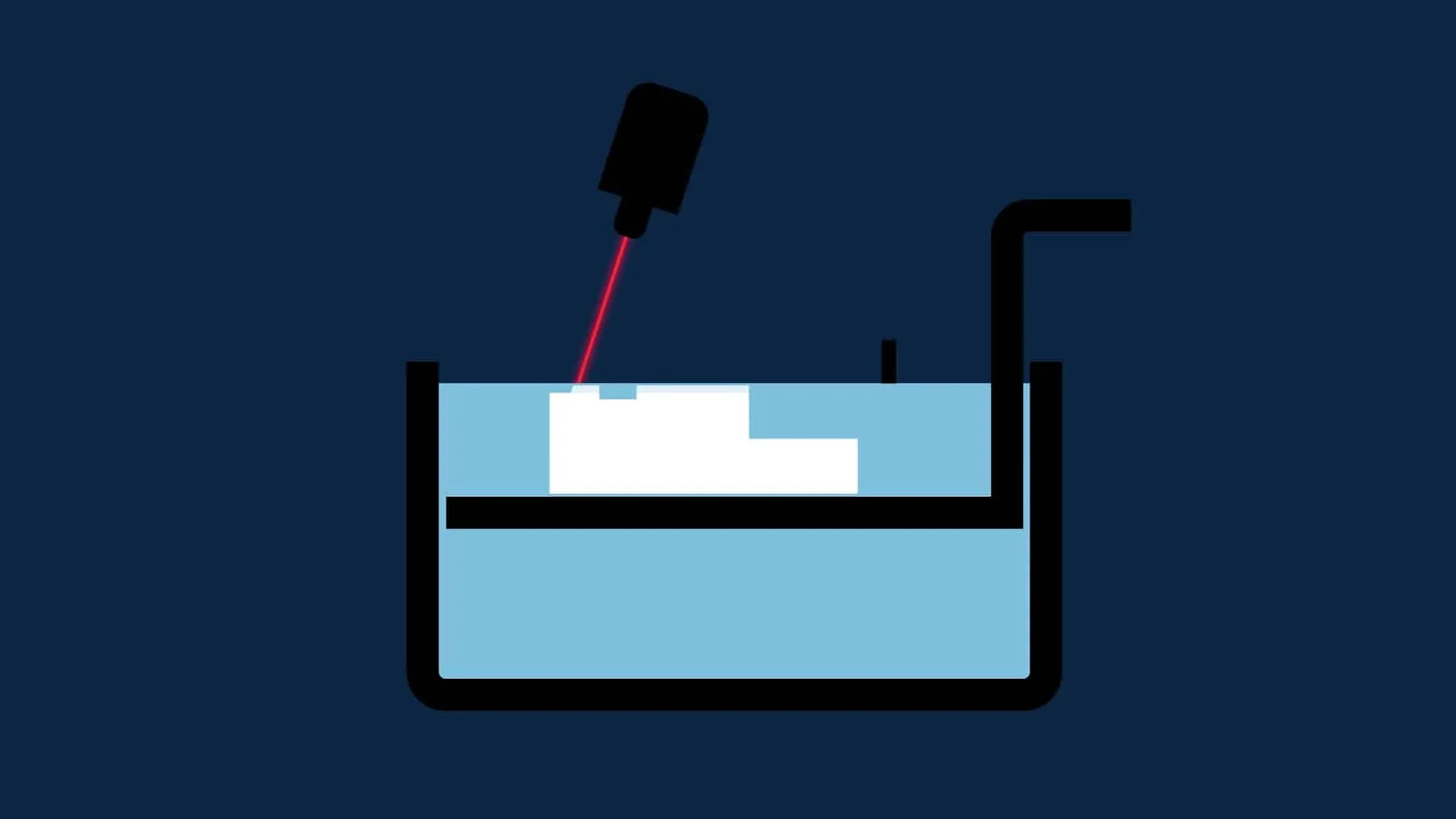
How does Photopolymerization work?
Photopolymerization is based on three elements. The first is the material tray containing the liquid photosensitive resin. The second is the heat source—either a UV lamp or laser—to photopolymerize the resin. The third is our printing plate which supports all the layers until we have the finished object. Once ready, we remove excess material using solvents. This is when we remove the substrates and detach the part from its tray before placing it in the oven for UV curing. This is how we solidify the part’s external surface.
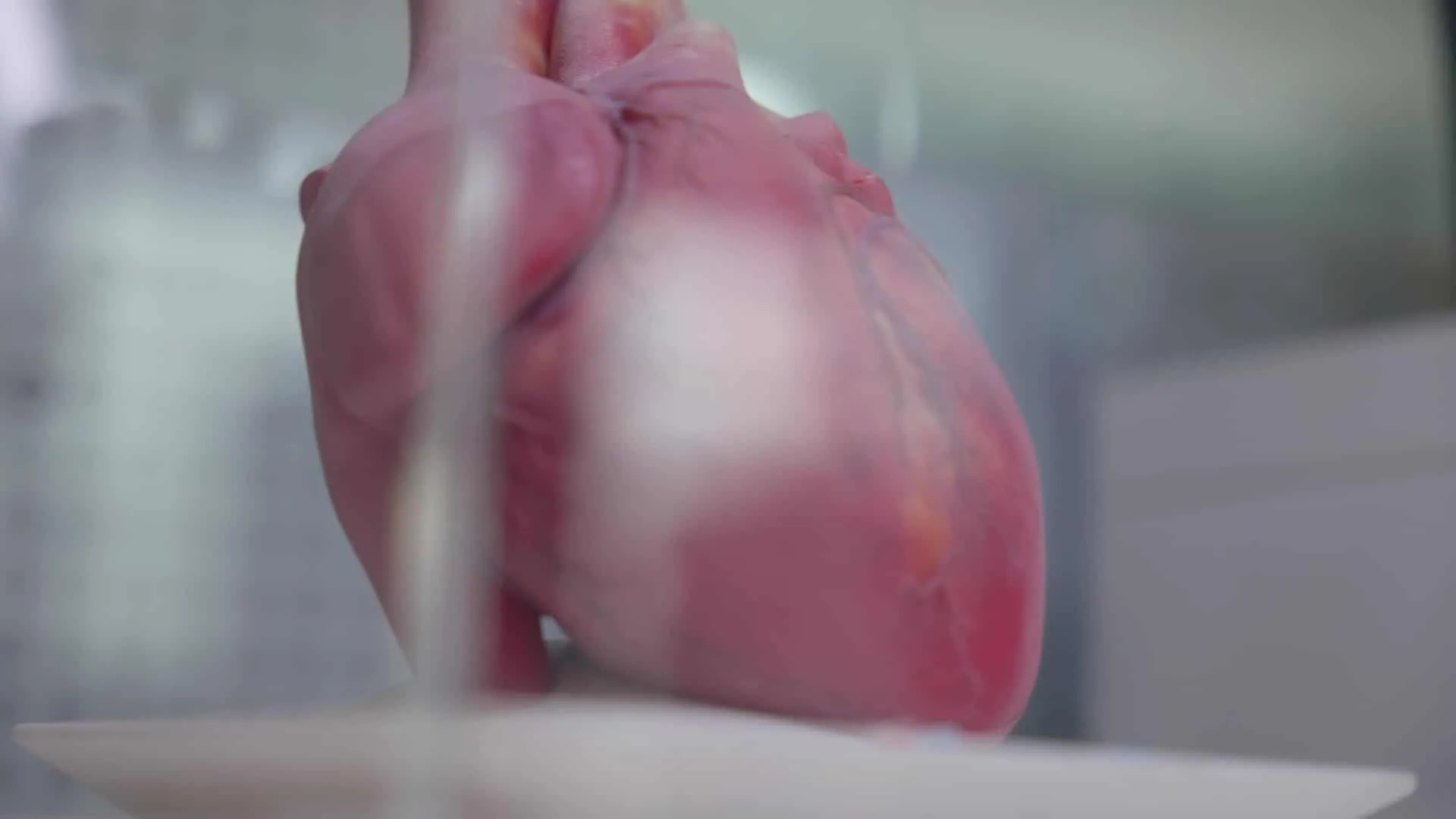
What are the advantages and usages of Photopolymerization?
Photopolymerization has the advantage of producing high-quality parts that require minimal finishing and less human effort. The drawback is that parts produced this way have lower mechanical resistance and high UV sensitivity. Photopolymerization has many uses; it’s also used for visual tests and marketing approvals, as well as in cosmetics and medical research.
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds