Video CNC Machining Turning
Find out in video how the CNC turning process works with 3DEXPERIENCE Make, the on-demand manufacturing platform, from Dassault Systèmes and its partner ACI Groupe.
Video What is Turning?
Hello. Today, we’re at MDV (ACI group) to talk about all things turning.
Turning is a sub-process of the machining family. It involves subtracting the excess material from a solid block of material until the final product is made.
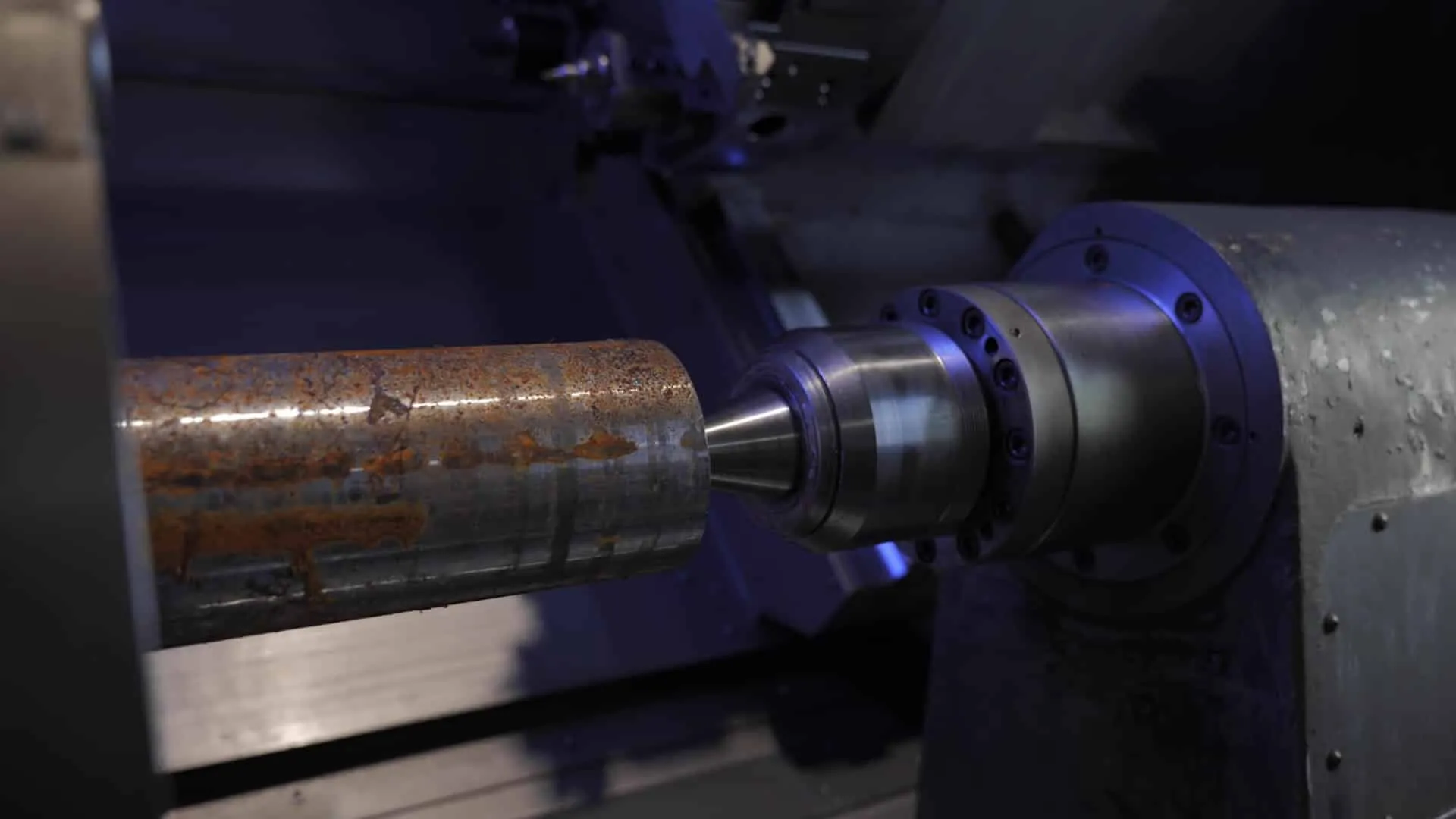
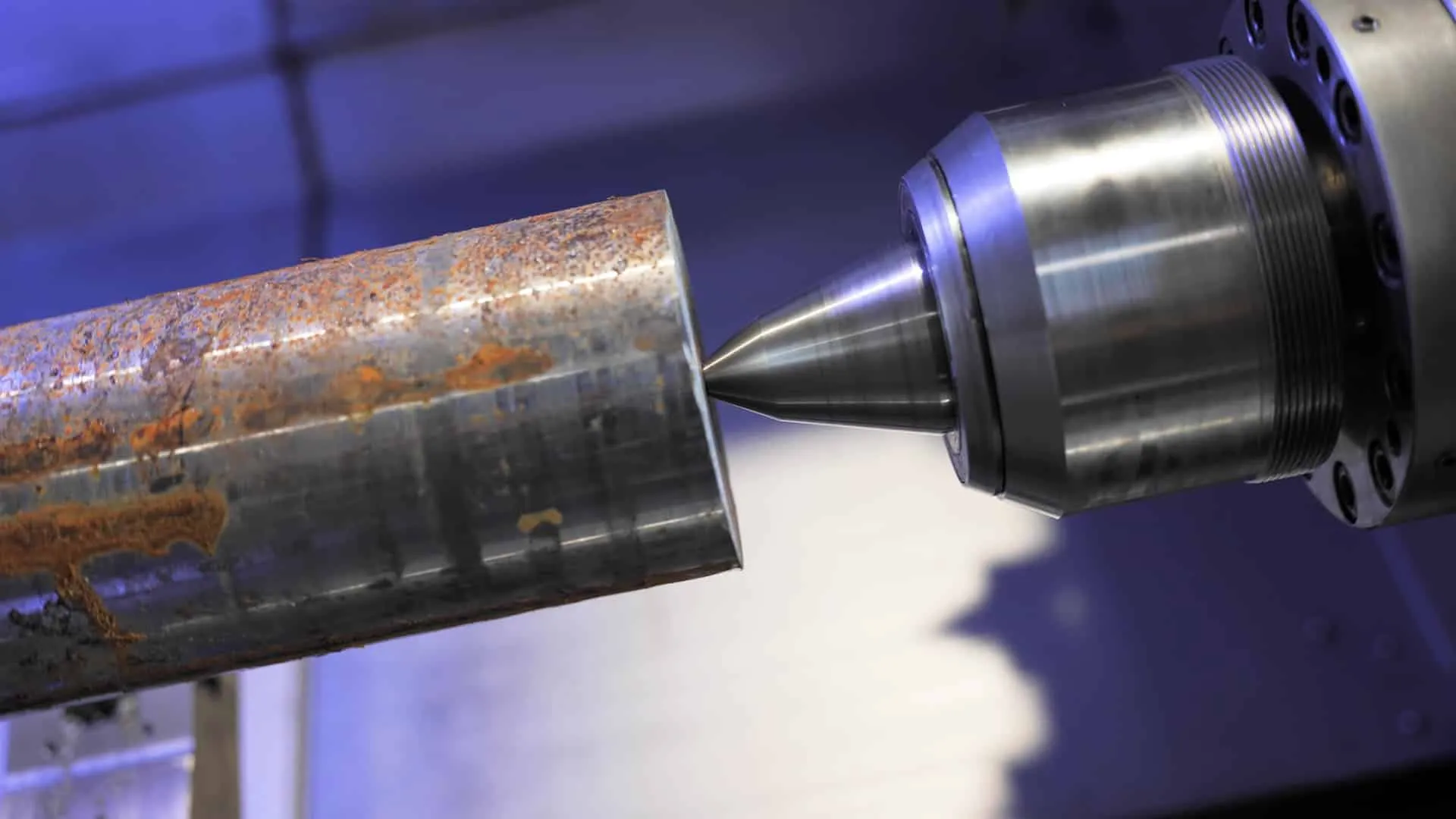


How does turning work?
In practice, turning consists of positioning a cylindrical block of material on an axis—mainly plastic or metal—in a machine called a lathe. The material is then turned in contact with a fixed tool to remove excess material until the final product is made. Turning machines have two axes to match the number of directions in which the lathe and machining part can move. Turning is either conventional or computer-assisted, also known as CNC turning. When the lathe is numerically controlled, it’s often deployed with milling capabilities to rework parts. This is what we call a milling lathe.
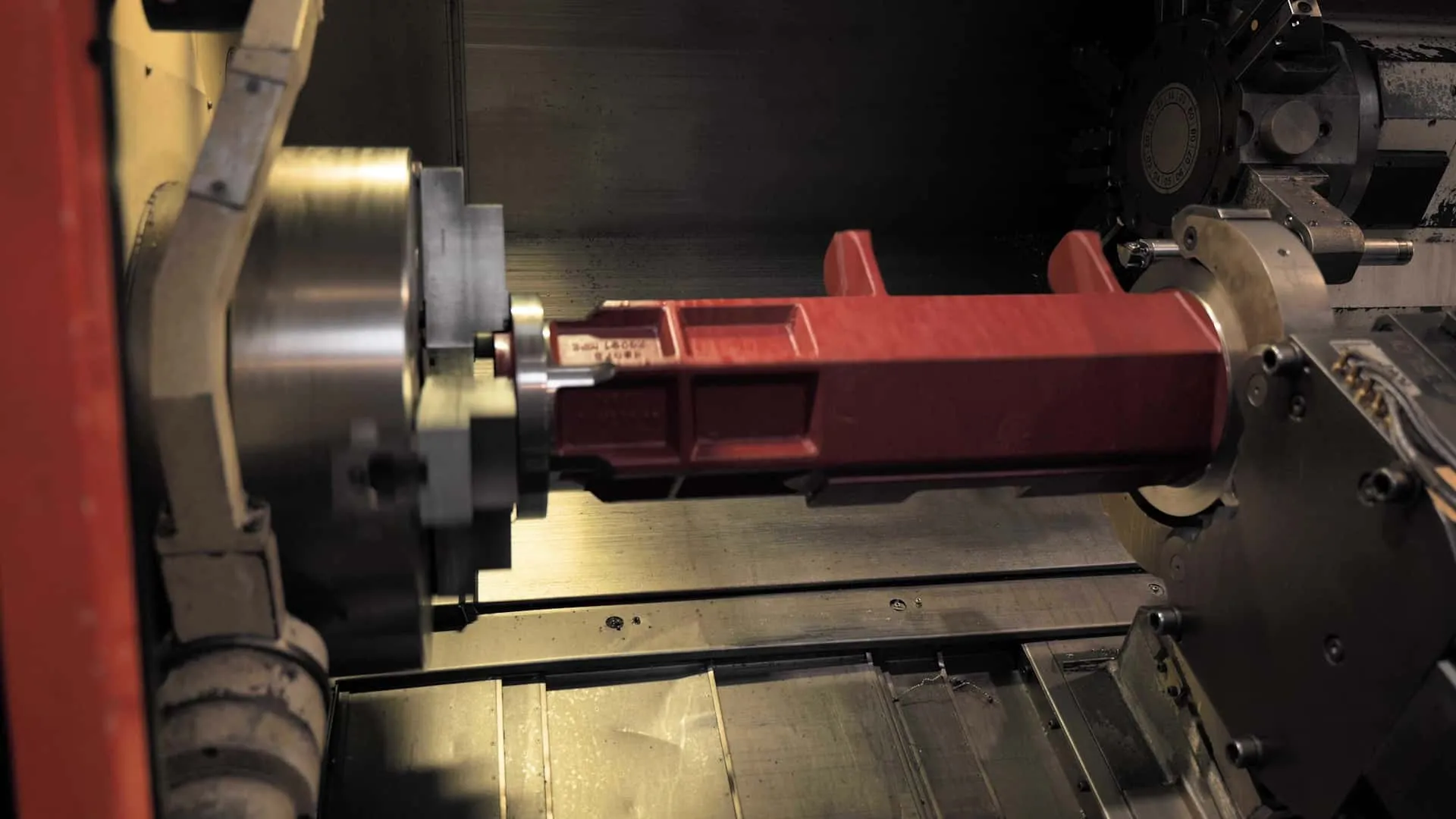
What are the advantages and constraints of turning?
Turning has one main drawback – you need to prevent tool vibrations. In the case of vibrations, tolerance won’t be respected, producing an ineffective surface.

What are the applications of turning?
Many industries such as automotive, aerospace, defense, and electronics deploy turning techniques.
Get multiple quotes for your parts in seconds
