Building the future with CAM, Computer Aided Manufacturing
Manufacturing any kind of product or machine used to be a long, intensive, imprecise, and complicated process that required input from a range of skilled craftspeople. Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) has revolutionized the means of production and given us the power to create precise, complex machinery and products.
What is Computer Aided Manufacturing Software?
As the name suggests, Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) involves replacing human interaction in the manufacturing process with computer controlled machinery. CAM allows us to create highly complex products quickly in a precisely uniform fashion.
Before the invention of CAM techniques, skilled engineers and machine operators had to set up manufacturing machinery and operate it to create products. The machinery followed a set of punch card instructions called ‘jigs’ that engineers would manually put in place. Operators and engineers then needed to manually drive the machinery and ensure that it followed the instructions The entire process was error-laden, slow, imprecise, labor-intensive, and expensive.
CAM was a revolution in terms of how we manufacture goods and machinery. In essence, CAM replaced the old-fashioned punch card jigs with a series of digital instructions which are sent to automated machinery via specialized software. The machinery can then automatically cut material and assemble parts to produce products.
CAM removes the possibility of human error, eliminates inconsistencies, and reduces the number of prototypes required during the design process. The entire manufacturing industry has been made more efficient, more accurate, and cheaper using CAM.
Discover the Computer Aided Manufacturing solutions from Dassault Systèmes
Dassault Systèmes specializes in developing sophisticated CAM, CAD, and PLM software solutions that give designers, engineers, and manufacturers the power to reimagine and reinvent how they create and produce.
How does CAM work and what are the different processes?
The CAM process is made up of various stages, each of which is intrinsic to the outcome. Each stage needs to be carefully planned and executed in order to avoid production mistakes that can result in manufacturing errors and product defects.
The design stage
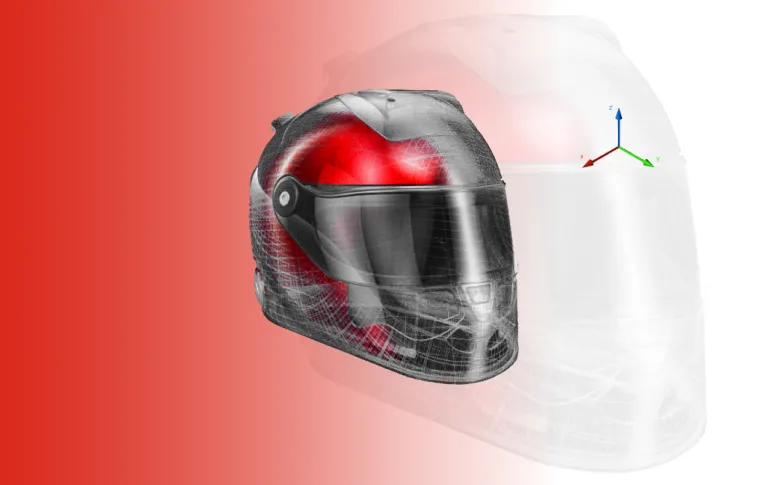
The CAM process begins with a designer or engineer developing a detailed 3D digital model that represents a proposed product or machine. The 3D model is constructed using specialized computer aided design (CAD) software, subjected to various tests and simulations and refinements are made.


The post-processing stage
Although CAM machines perform automated functions, they are not entirely autonomous. They require a set of instructions to follow. After the design has been finalized, CAM software checks the model to see if it has any errors that will impede manufacturing and then generates a toolpath that the CAM machinery uses to create the product.
These toolpath instructions are known as Computerized Numerical Control (CNC). CNC uses a machine language known as G-code. G-code controls a machine’s speed, its actions, the feed rate, as well as any coolants it requires, and so on. This is known as the post-processing stage.
The machine simulation stage
Before manufacturing commences, a machine simulation is run. This simulation is a digital representation of all aspects of the CAM process. It allows engineers to develop the most efficient method of producing a product and can be used for mechanical design.


The manufacturing stage
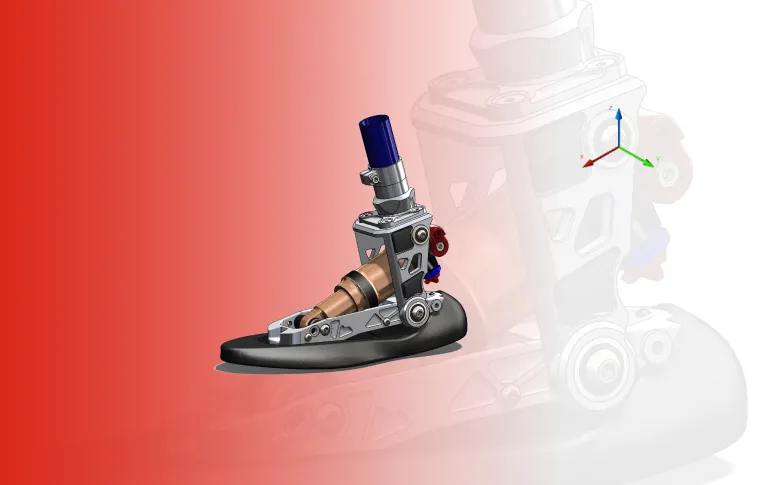
After the optimum manufacturing method has been identified, the actual process of manufacturing can begin. The CNC code is transmitted to the machinery via CAM software, raw materials are fed to the machinery, and the manufacturing process itself begins. Engineers will closely monitor the initial manufacturing run to identify any errors or defects. Rigorous quality control checks are required for each step of the process as well as on the final product.
What are the different types of CAM software?
As there are different stages of the CAM process, not all CAM software is designed for the same purpose. Engineers can make use of selected types of CAM software for specific roles. Some of the most common types of CAM software include:
Browse all the Dassault Systèmes store applications
We feature in our store some of our best software to design, collaborate and innovate throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Content related to Computer Aided Manufacturing
What are the advantages of using CAM?

There are many advantages to using CAM methods in comparison to older manual manufacturing techniques. The major advantage of CAM is that it allows manufacturers to produce highly predictable and consistent runs of products on any scale. CAM also allows for greater customization and increased design flexibility. This leads to improved product quality.
CAM software can analyze each stage of the manufacturing process and isolate the most efficient way to produce a product. This significantly reduces manufacturing costs and increases production speeds. Companies can produce goods for less in a shorter amount of time. Customers get better quality products for less cost. The optimization of the manufacturing process also results in better resource management and improved sustainability.
CAM has a positive impact on workers on the factory floor, as well. CAM software enables improved communication between colleagues which can help to ensure higher levels of productivity and enhance safety. Eliminating the need for workers to operate large, dangerous pieces of machinery greatly reduces the risk of injuries.
Common equipment used in CAM
The CAM process requires highly complex and sophisticated software that controls a range of precision-engineered CNC machines.
CAM is used to control a range of machines that shape and form workpieces, such as laser cutters, waterjet cutters, plasma cutters, and electrical discharge machining (EDM) machines. The highly cutting actions performed by these machines would not be possible without CAM.
Many factories producing goods with CAM techniques use advanced robotics to assemble products. This is common practice in the automotive, aerospace, and microchip industries.
Advances in additive manufacturing technology have seen the uptake of 3D printers by more companies than ever before. Although still very much in the early stages of development, experts predict that additive manufacturing will be used widely in the near future.

What are the latest CAM industry trends?

As well as the development of 3D printing and additive manufacturing, there are other new developments in the CAM industry. Digital twin technology is allowing engineers to produce highly accurate representations of factory layouts, giving them essential data with which they can better optimize manufacturing techniques.
Advances in cloud computing technology and the Industrial Internet of Things are driving the development of Industry 4.0. Experts predict that manufacturing facilities will no longer be seen as standalone enterprises but will be closely interlinked and be able to share information on processes and resources in real-time. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, sensor technology, augmented reality, and big data analytics are all poised to usher in a new era of CAM.
CAM - Conclusion & Perspectives
Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) has revolutionized how we produce products and machinery. Using highly sophisticated CAM software and machinery, we can produce products in less time, for less cost, and with less waste in safer and more sustainable ways than ever before.
CAM techniques remove the likelihood of human error and enable the production of precisely engineered, uniform products on any scale. It is no exaggeration to say that modern life simply would not be possible without the advent of CAM.
Despite the reliance of CAM on technology and machinery, it still requires the human touch. Applying CAM techniques successfully relies on the efforts of skilled and talented engineers, operators, and designers to design products, optimize production methods, and control production. To do so effectively, these experts all use CAM, PLM, and CAD software developed by innovative companies such as Dassault Systèmes.
Why choose Dassault Systèmes for Computer Aided Manufacturing your needs?
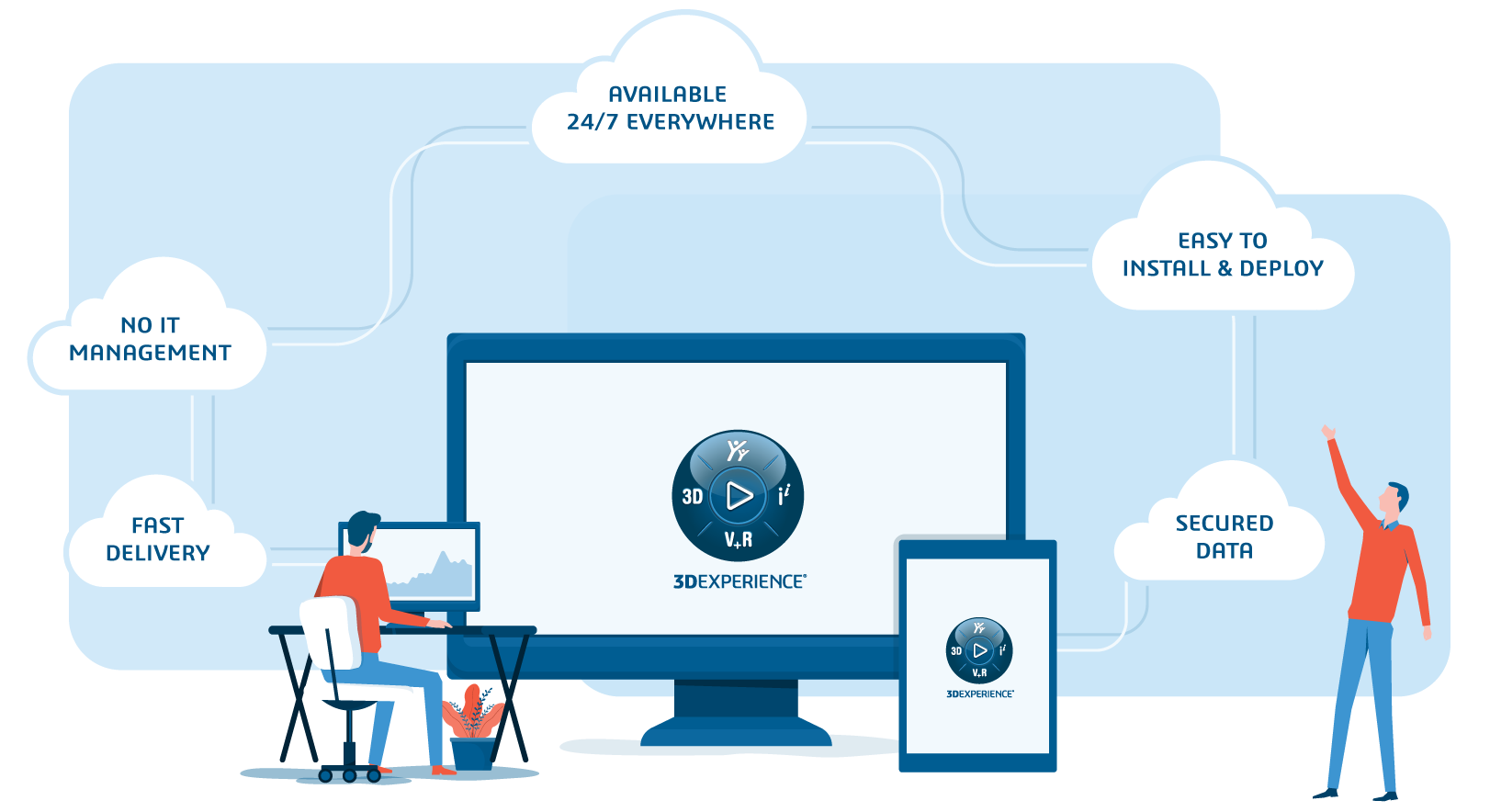
Break away from IT restraints with the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform
The 3DEXPERIENCE Platform gives users the ability to store and share files, communicate and collaborate with colleagues, and get access to a range of powerful CAD, CAM, and PLM software via one secure, fully integrated digital environment. All you need to access the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform is an internet-enabled device with a compatible browser.
Enhance your productivity, drive innovation, and break away from the restraints of traditional technology with the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform.

Partner with CAM experts with more than 40 years of experience
Reaching new levels of innovation and discovering better ways to manufacture products is only possible with the right tools. For more than four decades, manufacturing experts and professional engineers have turned to Dassault Systèmes for powerful, intuitive, and effective CAM, CAD, and PLM software.
Dassault Systèmes is committed to providing solutions that will enable manufacturing companies to produce better quality products in less time, using fewer resources than ever before. Our goal is to empower our clients with the tools they need to meet and overcome the challenges of the modern world.
Dassault Systèmes is made up of 11 brands dedicated to providing customized solutions to help professional engineers and designers to create, innovate, and collaborate more easily, more efficiently, and more effectively. Discover the entire range of Dassault Systèmes roles today.