Explore the Capabilities of Professional 3D Rendering Software
High-quality images made using 3D rendering software appear in films, advertising, magazines, and social media. We explain exactly what 3D rendered images are, why they are so popular, and what rendering software the experts choose.
What is 3D rendering?
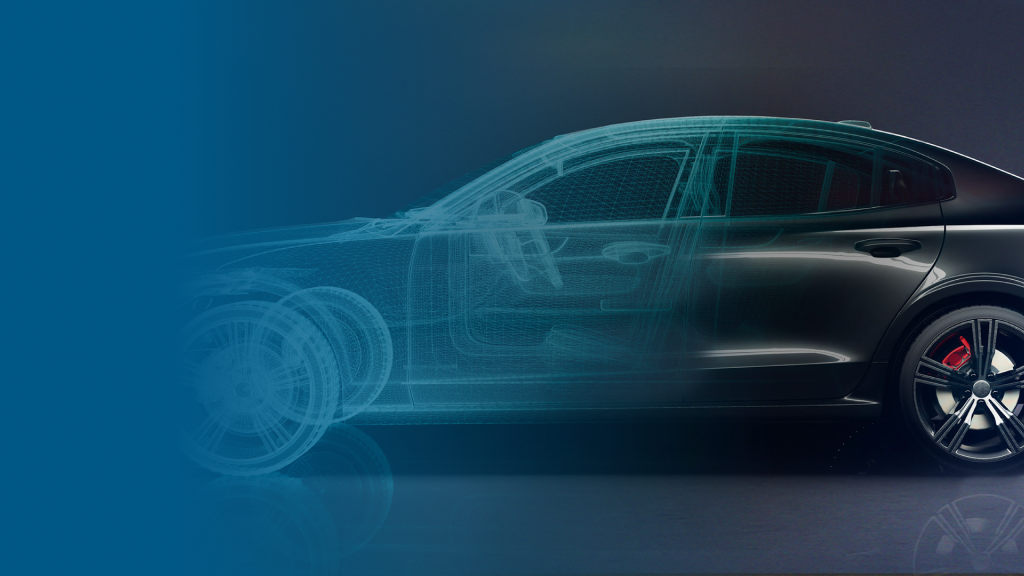
Let’s start with the most obvious question: what is 3D rendering? In simple terms, a 3D render is a high-quality 2D image of a three-dimensional computer generated model. You can think of a 3D render as being somewhat like a photograph, except that a 3D render depicts a digitized object, instead of a physical one. 3D renders can be created to look exactly like real objects, or they can be purposely made to look non-realistic. Photorealistic 3D rendering is often used in advertising, education, product development, and other purposes that require visuals with a high degree of realism.
These images are so finely detailed that it is often impossible to tell the difference between a photorealistic 3D rendered image and an actual photograph. On the other hand, non-realistic 3D rendered images are intentionally not supposed to look like real objects. These images are often cartoon-like or fantastical. Non-realistic 3D rendered images are highly stylized and based on traditional artistic techniques like drawing or painting. They are commonly used in artworks, animation, and video games. If you are interested in creating such images, you might want to consider using a professional software like DraftSight Professional.
Discover exciting 3D rendering solutions from Dassault Systèmes
With 3DEXITE Product Communicator you can produce highly detailed 3D models and photorealistic or non-realistic 3D rendered images. 3DEXITE Product Communicator is the ideal tool for product development, animation, interactive simulations, and virtual reality experiences.

3DEXCITE Product Communicator
Seeing is believing - create stunning digital content to showcase product values, enable partners and win customers

3D Publication Credits
Use 3DEXCITE xStudio and cloud rendering to generate photorealistic renderings on any device
How does 3D rendering work?
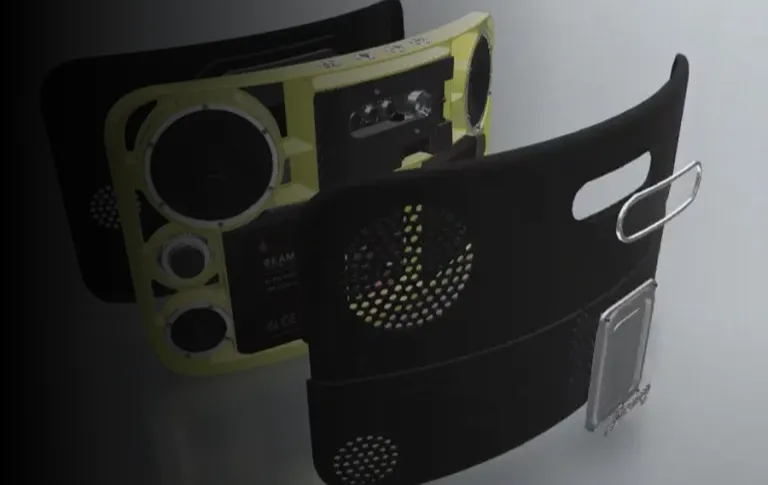
To create a 3D rendered image, a designer first needs to use CAD design software to create a 3D model. This model is refined by adding lighting details and complex textures. The designer will then use dedicated CAD rendering software to take the data from the 3D model and transform it into a high-resolution 2D image. The designer may then choose to further refine the 3D rendered image with additional textural or lighting details to embellish its features.
- The 3D rendering process, an example
- The difference between 3D rendering and 3D visualization
- The difference between 3D modeling and 3D rendering
You can think of the 3D rendering design process in this way: Imagine a sculptor making a statue. The sculptor does this by forming a ball of clay into the desired shape. Once it has been completed, the statue exists in three dimensions, so it can be viewed from any angle. The sculptor can improve the statue by adding details such as coloring or textures to make it more lifelike or to exaggerate its features. These first steps are representative of the 3D modeling and texturing process.
The sculptor decides they wish to photograph the statue. The statue is placed in front of a background and the lighting is carefully arranged. The camera captures an image that shows how the light reflects off the statue. This is indicative of how 3D rendering software generates a 2D image from a 3D model.


The term 3D visualization is used to describe the entire process of creating a realistic digital image. 3D rendering is one of the last steps in the visualization process.
As we can see from the example above, 3D modeling is the process of creating a digital model that replicates a real object. 3D rendering is the process of taking that 3D model and creating a high-quality 2D image from it.

How 3D rendering is used today
What is 3D rendering used for? A wide variety of industries use 3D rendered images to communicate with customers and colleagues. Because 3D images are able to show incredibly detailed and lifelike representations of any object, they are used by almost every type of business imaginable.
- Television, film, and video games
- Architecture and Construction
- Industrial design and product development
- Advertising and marketing

Originally, 3D rendering was used mostly by television, film, and video game companies for animating characters and creating special effects. It now plays a fundamental role in creating captivating visual sequences. Animation sequences are created by compositing several 3D rendered images together. Blockbuster movies, children's television programs, and best-selling computer games seamlessly integrate visual effects crafted by sophisticated 3D visualization software, employing advanced techniques such as ray tracing for lifelike renderings.
The way we design, build, and decorate our homes and offices has been drastically changed by 3D rendering. Architectural companies now use photorealistic renders to provide clients with detailed visualizations of proposed building projects. Interior designers can create realistic mock-ups of how a room may look. Some 3D CAD rendering programs allow designers to create virtual tours of buildings.


Photorealistic product rendering allows the industrial design process to be faster and more cost-effective than ever. Designers and engineers utilize 3D models and renders to exhibit and assess products, components, and machinery without the necessity of physical prototypes, employing advanced graphics and animation techniques to simulate real-world effects.
3D rendering product images are also often used in advertising and marketing. It is usually quicker and much less expensive to produce a 3D render than to stage a photo or video shoot.

The different types of 3D rendering software
- CPU-Based 3D Rendering Software
- GPU-Based 3D Rendering Software
- Hybrid 3D Rendering Software
- Cloud-Based 3D Rendering Software
CPU-Based 3D Rendering Software
This software creates 3D rendered images by using the power of a computer’s inbuilt central processing unit (CPU).

GPU-Based 3D Rendering Software
Much the same as CPU-based 3D rendering software except these programs use the computer’s graphics processing unit (GPU). GPU rendering can be faster than CPU rendering. However, CPU rendering allows for the use of more features which makes it better for photorealistic renders.
Hybrid 3D Rendering Software
This software combines CPU-based 3D rendering and GPU-based 3D rendering by using both of these components to produce 3D renders. V-Ray is an example of a well-known hybrid rendering program.
Cloud-Based 3D Rendering Software
Rendering in the cloud allows designers to harness the power of multiple computers instead of relying on one machine. Cloud rendering is significantly faster than both CPU and GPU rendering.
Browse all the Dassault Systèmes store applications
We feature in our store some of our best software to design, collaborate and innovate throughout the entire product lifecycle.
Global illumination & Ray casting
Global Illumination, Path Tracing, and Ray Casting Explained
Product rendering
The process of product rendering and 3D visualization explained
Cloud rendering
Global Illumination, Path Tracing, and Ray Casting Explained
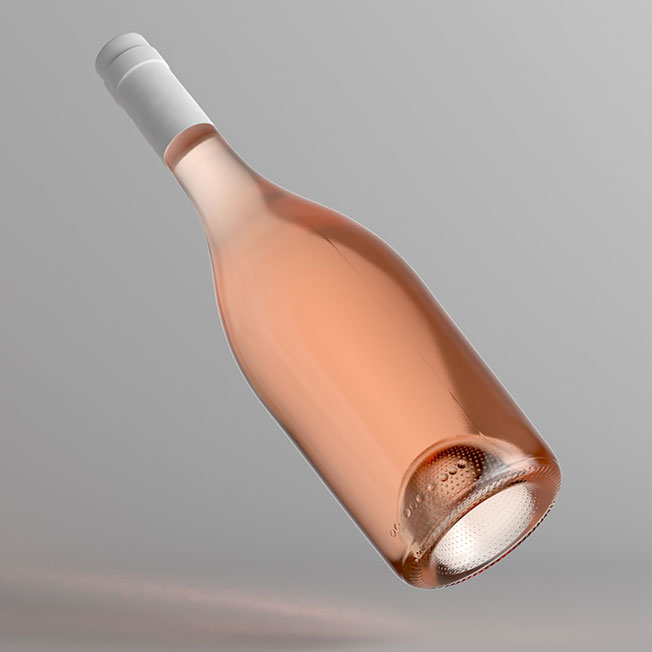

The benefits of 3D rendering
You may be wondering just why would a company choose to produce a 3D rendered image rather than a drawing or a photograph. While traditional drawings and photos still have their place, it turns out that there are several benefits to using 3D rendered images.
The amount of control that a designer has over every aspect of the image can result in more realistic and incredibly precise depictions of an object. For instance, a 3D rendered image allows designers to have absolute control over the lighting. There’s no need to wait for perfect conditions or waste time setting up a lighting rig.
Using a 3D rendered image enables designers to create exact visualizations of objects before they are physically created. Every feature of a proposed product or building can be represented in the finest detail. This drastically increases the marketing potential, allows for faster design iterations, and cuts development costs.
Common 3D rendering techniques
The history of 3D rendering
- The early beginning
- The modern history of 3D rendering
- 3D rendering becomes widespread
The early beginning
Architects, engineers, and artists were using wireframe models and illustrations to plan out their creations as far back as the Italian Renaissance. Metal wires were used to build three-dimensional objects that provided a visual guide for buildings and equipment. These rudimentary wireframe models were to form the basis for the powerful CAD software that was to come.

The modern history of 3D rendering
The modern history of 3D rendering starts in the 1960s and 1970s when computer programmers developed software that could replicate physical wireframe models. The Sketchpad program by A. Sutherland was the first instance of digital 3D modeling.
This concept was refined in the 1970s by researchers at the University of Utah, including Martin Newell who employed sophisticated 3D modeling techniques to create the now iconic ‘Utah teapot’. Further advances came with the development of the z-buffer algorithm by Ed Catmull and Turned Whitted’s work on recursive ray tracing.

3D rendering becomes widespread
In the 1980s, binary space partitioning (BSP) trees, texture models, and blobby mapping were introduced by American computer scientist Jim Blinn. These innovations led to the widespread use of 3D rendering in animation, although other industries soon saw the potential of the technology.
The 80s saw the rise of 3D rendering in architecture, most notably by Zaha Hadid who used CAD visualizations and 3D rendering for her 1983 design of The Peak Leisure Club in Hong Kong. Before long, the majority of architects, construction experts, and industrial designers were turning away from their pencils, paper, and drafting tools and towards CAD software and 3D rendered images.
With the development of more powerful computers and software, 3D rendering became widespread in the 1990s. The movie Toy Story was released and quickly shot to fame as the first film made using 3D rendering. The 1990s saw video games move from pixelated artwork to completely 3D rendered graphics.
By the dawn of the millennium, 3D rendered images were commonplace and being used for everything from social media advertising to big screen special effects to architectural models and product prototypes.


The future of 3D rendering
Just as it would be impossible for someone in the 1960s to imagine how the simple wireframes of Sketchpad would lead to the innovations of today, it is difficult to precisely say what the future holds for 3D rendering. However, we can make a few educated guesses as to what developments may occur in the coming years.
As technology advances, we are sure to see increasingly hyper-realistic 3D rendered images surpassing even the highly sophisticated images we have now. Future developments in 3D rendering will allow us to experience realistic, completely immersive digital environments. Augmented reality and virtual reality are sure to expand the ways in which 3D visualizations can be utilized as entertainment, as educational tools, and for architectural and product design purposes.
3D rendering, conclusion and perspectives
In modern life, we are literally surrounded by 3D rendered images. 3D images fill our visual space as we watch our televisions, learn new concepts, browse social media, flip through magazines, or relax while watching movies or playing video games.
The flexibility and versatility of 3D rendering software give professionals the power to develop new ways of designing products, create mind-blowing entertainment, and construct more sustainable and resource-efficient vehicles and buildings. 3D rendering is now a crucial tool for an incredibly diverse range of industries such as healthcare, architecture, graphic design, and aerospace, to name but a few. It is clear that the power of 3D rendering will continue to shape our world.
Explore Dassault Systèmes solutions
Discover the powerful browser-based modeling solutions from Dassault Systèmes. You can design whatever you wish, wherever you are with 3DEXPERIENCE.
Connecting data & people to foster innovation
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform on the cloud gives you access to a various set of applications that allow you to design, simulate, inform and collaborate on a project.
Why choose Dassault Systèmes for your 3D rendering needs?
3DEXITE Product Communicator and the 3DEXPERIENCE platform
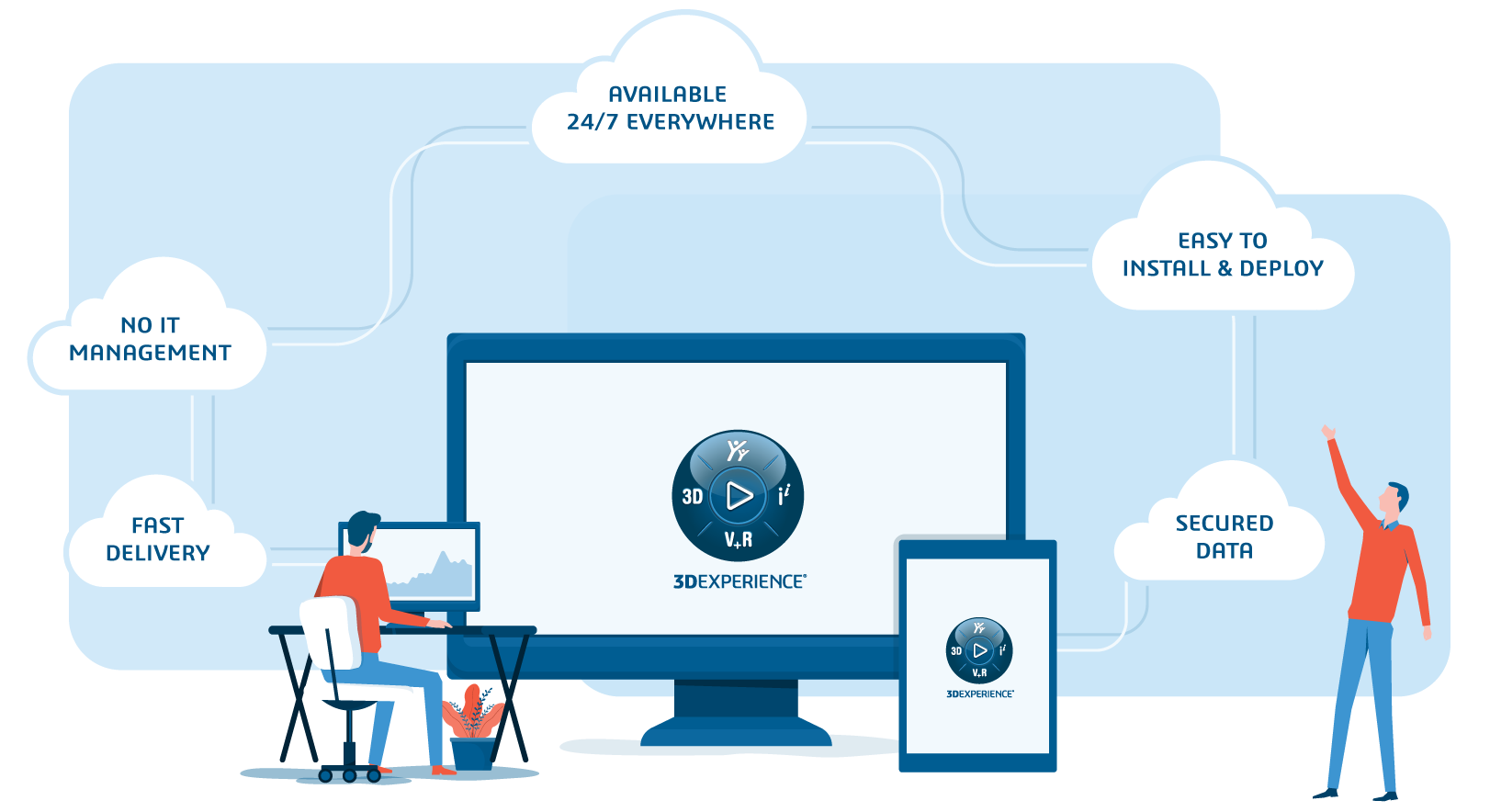
Using the 3DEXPERIENCE platform in conjunction with 3DEXITE Product Communicator gives designers the ability to securely store and share files and collaborate with team members at any time, on any device, anywhere in the world.
3DEXITE Product Communicator integrates fully with all 3DEXPERIENCE, giving you more scope, power, and functionality than any other program on the market. The intuitive and user-friendly interface allows even novice designers to create and share quality 3D models and 3D rendered images.

Partner with a world leader in 3D rendering software
For more than 40 years, Dassault Systèmes has been at the forefront of CAD design software. Our range of innovative and powerful solutions enables engineers, designers, and artists to bring their visions into reality and discover new, previously unattainable possibilities. From the automotive sector to the construction industry to renowned digital artists, Dassault Systèmes software is used by design experts across the globe.
Whether you are a beginner or a seasoned professional, Dassault Systèmes can provide you with exceptional 3D rendering software. Find the design solutions that you’ve been searching for. Explore the entire range of Dassault Systèmes CAD applications today


