Wave6 Industry Applications
Wave6 Noise and Vibration Analysis Applied in Industrial Development Processes
Technical Excellence in Noise & Vibration Analysis
Noise and vibration analysis is becoming increasingly important in virtually every industry. The need to reduce noise and vibration can arise because of government legislation, new lightweight constructions, use of lower-cost materials, detectability, fatigue failure or increased competitive pressure. Wave6 is ideal to evaluate noise and vibration performance during the design stage for a wide range of industries. It helps in reducing the risk of discovering expensive problems late in the design cycle when physical prototypes become available.
Applications of Noise and Vibration Analysis
Explore the multifaceted applications of Wave6 in noise and vibration analysis across various industries. The prominent industries that reap Wave6’s benefits include Aerospace & Defense, Consumer Goods, Marine & Offshore, and Transportation & Mobility. This overview offers the intricacies of Wave6 capabilities for each sector, from reducing interior aircraft noise to optimizing loudspeaker designs, and discovers how Wave6 contributes to precision analysis, safeguarding innovation and compliance with industry standards.
- Aerospace & Defense
- Marine & Offshore
- Transportation & Mobility
- Other
Aerospace & Defense
- Interior noise in aircraft, rotorcraft and EVTOLs
- Optimization of damping treatments on fuselages accounting for pressurization, stress stiffening and non-uniform temperature
- Design of isolators and sound package
- Design of PA systems and full spectrum models of speech transmissibility and speech intelligibility
- Full spectrum methods for assessment of noise exposure for ground crew
- Design of liners in engine nacelles, accounting for non-uniform temperature, pressure, density and mean flow
- Incident acoustic wave source models for annular ducts with non-uniform mean flow
- Propeller noise source models that account for both thickness and loading noise, for both interior and exterior acoustics, including import of unsteady time domain CFD data
- Models of noise sources, propagation and attenuation in Environment Control Systems
- Advanced wave-based SEA modeling of fuselages and fairings with rigorous models of wave propagation and scattering
- Acoustic qualification testing of spacecraft and launch vehicles
- Advanced accelerated Boundary Element Methods for large fully coupled FE-BEM models of spacecraft and launch vehicles, including solving large models on modern high-performance computing (HPC) clusters
- Extensive library of loads for modeling excitation from liftoff, aerodynamic loading and random diffuse acoustic field excitation
- Advanced loudspeaker and loudspeaker array models for modeling Direct Field Acoustic tests, including integrated calibrated loudspeakers from Acoustic Research Systems
- New methods for full spectrum modeling of shock sources and shock response, including modeling of pyrotechnic devices and frangible joints, shock propagation and attenuation through built up structures and characterization of shock responses for sensitive components
Marine & Offshore
- Full spectrum system-level models of noise and vibration in ships and submarines
- Modeling of noise and vibration to hull structures through primary and flanking paths
- Modeling transmission of fluid-borne waves in piping systems
- Modeling acoustic radiation from gearboxes and pumps
- Design of isolation and absorption to minimize airborne and structure-borne noise from machinery components
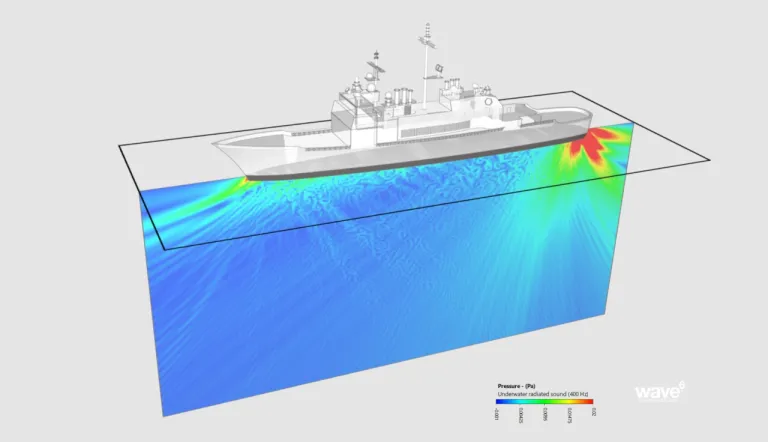
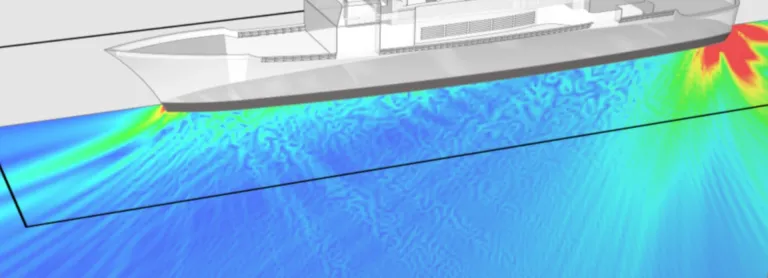
- System and component level models of underwater radiated noise accounting for heavy fluid loading effects
- Modeling sonar systems, including sonar self-noise
- Modeling acoustic scattering from large coated hull structures, including the effects of multiple scattering
- Ensuring quiet interiors in luxury cruise ships and yachts
Transportation & Mobility
- Acoustic radiation from powertrain components
- Design of acoustic covers and encapsulation
- Accurate modeling of both structure-borne and air-borne noise in large trimmed body structures
- Unique new methods for modeling noise from treaded tires
- Full spectrum modeling of audio and infotainment systems (including binaural and VR-based auralization)
- Detailed models of wind noise (complement existing wind noise models by adding detail to various paths including greenhouse and underbody wind noise)
- Diagnose flanking transmission and damping from seals
- Quick models of fans and blowers
- Model exterior acoustics and pass-by noise
- Sound package design and optimization (including parametric and non-parametric optimization of sound package)
- Full spectrum models of acoustic radiation, insertion loss, transmission loss and absorption
- Optimization of viscoelastic damping and mastics
- Inverse methods for source characterization
- Design of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, intakes and exhausts (including shell noise and accurate modeling of non-uniform temperature, pressure, density and mean flow)
Other
- Modeling interior and exterior noise in industrial equipment cabs
- Modeling interior and exterior noise in trains
- Modeling noise from horns to meet regulatory requirements
- Modeling noise from gearboxes and towers in wind turbines
- Modeling noise in elevators and escalators
- Modeling noise from HVAC systems and industrial chillers
- Modeling noise in mobile phones and electronic equipment
- Assessing and improving the sound quality of golf club drivers
- Detailed modeling of loudspeakers and headsets, including 2-way coupling between electrical and mechanical components
- Reducing noise and vibration of healthcare equipment such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, dialysis machines etc.
- Assessing noise in factories to meet legislative requirements for interior and exterior noise
Also Discover
Learn What SIMULIA Can Do for You
Speak with a SIMULIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right SIMULIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering