Abaqus/Standard
Solution Technology for Linear and Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis
Discover the Abaqus/Standard Advantage
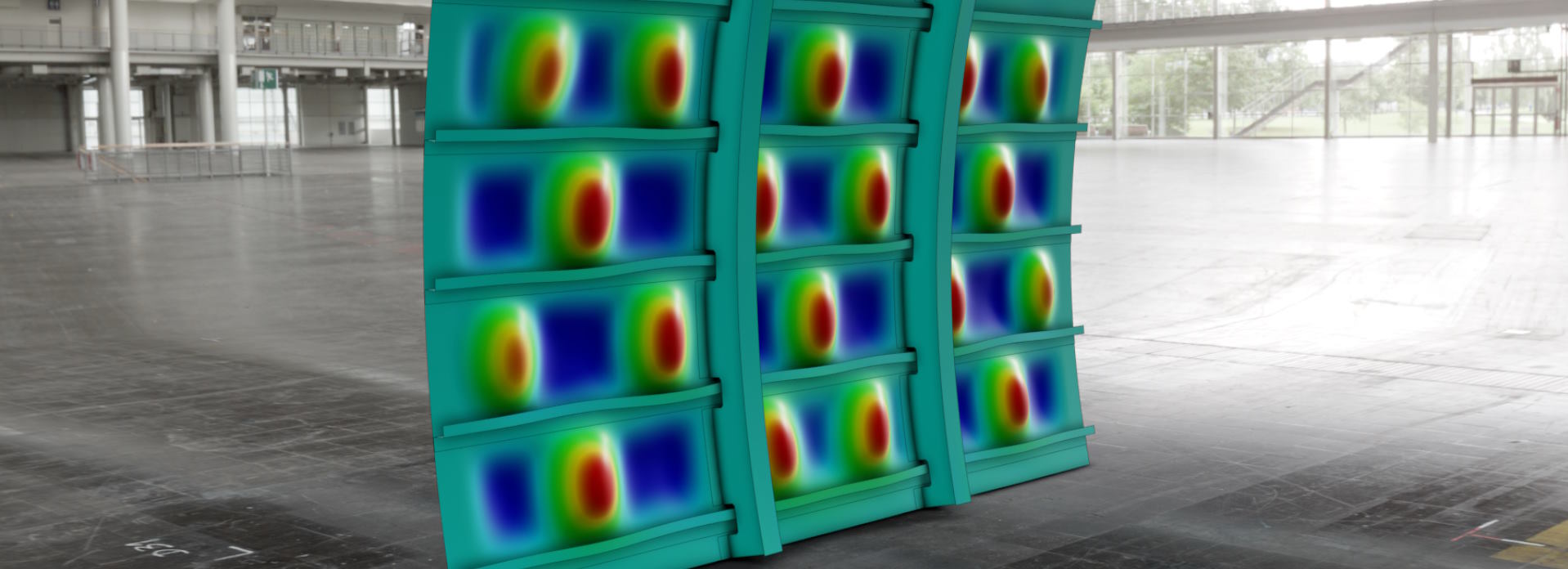
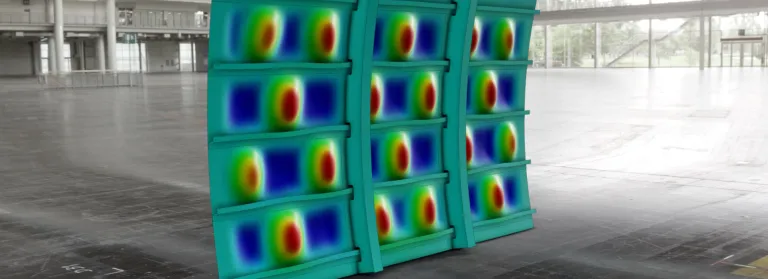
Abaqus/Standard is a general-purpose finite-element solver that simulates true static and structural dynamic events. Its applications include thermal stress analysis, sealing evaluations, steady-state rolling simulation, fracture mechanics studies, heat-transfer modeling, acoustics, pore pressure, and more.
Abaqus/Standard has powerful linear dynamics capabilities, including the AMS EigenSolver, which efficiently identifies numerous natural frequencies for models with various degrees of freedom. It also has a curated library of elements accessible to users for its wide range of applications and an extensive library of material models ranging from linear elasticity to rate-dependent kinematic plasticity to continuum damage.
Users can customize and extend Abaqus/Standard by coding subroutines for material models, elements, loads, and boundary conditions. The Abaqus/CAE modeling environment supports Abaqus/Standard for all typical pre- and post-processing requirements.
Abaqus/Standard and Abaqus/Explicit are designed to work cohesively, allowing you to couple the two solvers. You can continue a simulation that starts in Abaqus/Explicit, in Abaqus/Standard and conversely. The importing functionality allows users to apply Abaqus/Standard to those portions of the analysis well suited to an implicit solution technique. Alternatively, users can apply Abaqus/Explicit to those portions of the analysis where high-speed, nonlinear, transient response dominates the solution.
- Analysis Types
- Element Types
- Material Models
Analysis Types
- Nonlinear static and dynamic stress analysis
- Linear dynamics, which include a highly efficient AMS EigenSolver
- Heat transfer
- Acoustics
- Multi-physics procedures for
- Thermal/structural simulations
- Thermal/structural/electrical simulations
- Battery simulations
Element Types
- Linear and quadratic solid elements for stress analysis
- Structural elements: Shell elements, beam elements, truss elements, membrane elements
- Elements for coupled simulations
- Thermal/structural elements
- Thermal/structural/electrical elements
- Piezoelectric elements
- Pore pressure elements
- Thermal/electrochemical elements for the simulation of battery cell
- Special elements for modeling
- Gaskets
- A wide range of kinematic behaviors
- Spot welds
- Adhesive connections
Material Models
- Linear elasticity and viscoelasticity
- Nonlinear viscoelasticity
- Isotropic and kinematic plasticity
- Damage and fracture mechanics
- Multiscale and Mean-Field Homogenization
Start Your Journey
Explore the technological advancements, innovative methodologies, and evolving industry demands that are reshaping the world of Static and Low Speed Dynamic Events Simulation. Stay a step ahead with SIMULIA. Discover Abaqus Standard now.
FAQs About Linear Dynamics
Dynamic systems are systems that change over time according to specific rules.
Linear dynamics refers to systems where changes are directly proportional to inputs and the current state, making their behavior predictable. These systems are simpler to analyze than nonlinear ones, as they follow straightforward, proportional relationships.
Nonlinear dynamics refers to the study of systems that do not follow a direct cause-and-effect relationship, where small changes in initial conditions can lead to vastly different outcomes, often analyzed through differential equations.
Linear dynamic analysis is a method used in structural engineering to assess how structures respond to dynamic, time-varying loads. It assumes that the relationship between the loads and the structural response is linear.
To solve a linear dynamical system, you perform step-by-step time integration of the equations of motion, defining material properties, boundary conditions, and initial conditions. Choose an appropriate analysis procedure (modal, harmonic, transient, or steady-state dynamics) based on the loading and response. Software like Abaqus/Standard can discretize the model and solve the linear equations for each time step, providing the system's response over time.
Also Discover
Learn What SIMULIA Can Do for You
Speak with a SIMULIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right SIMULIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering