fe-safe
Durability Analysis Software for Finite Element Models
Material Efficiency in Industry
Material usage optimization has become the cornerstone of the transformation that the industry is currently experiencing. Manufacturers relentlessly pursue lightweight and robust components to deliver cost-efficient production with lower warranties, minimal recall costs, and accelerated timelines. Advanced finite element analysis is a staple in design stress calculations. Many companies still rely on manual stress point selection for spreadsheet analysis to conduct fatigue analysis. This approach is time-consuming and unreliable because it increases the risk of overlooking critical failure locations.
FEA Fatigue Analysis
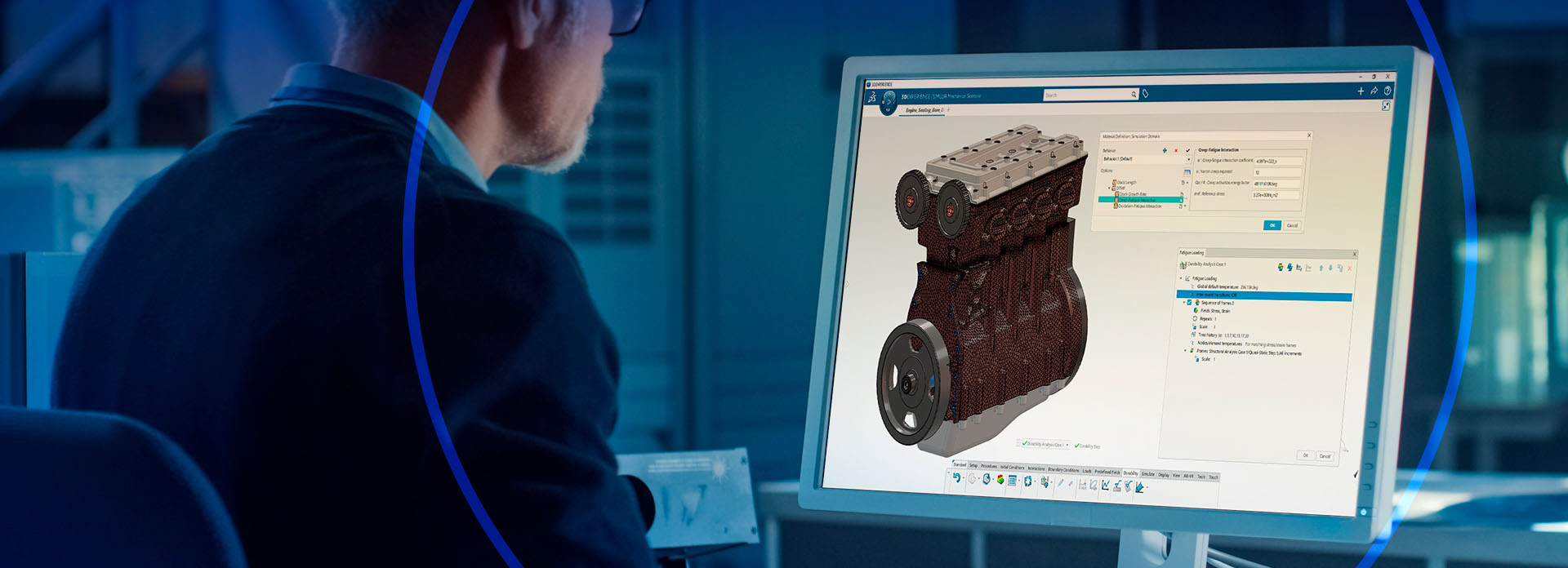
fe-safe is the technical leader in fatigue analysis software for finite element models. fe-safe has set the benchmark for fatigue analysis software since the early 1990s in close collaboration with the industry. The fe-safe software suite is a world-leading technology for durability analysis from FEA. It directly interfaces with all major FEA suites (Abaqus, ANSYS, Nastran) and can meet the most demanding industry applications.
Fatigue Analysis Methods
fe-safe was the first commercially available fatigue analysis software to focus on modern multiaxial strain-based fatigue methods and it continues to set the benchmark for fatigue analysis software. Extended Packaging includes fe-safe, allowing unified access to all solution technologies within the portfolio through a single token pool. fe-safe is popular for its accuracy, speed, comprehensive capabilities and ease of use. Regardless of the complexity of your fatigue analysis, fe-safe fits smoothly into your design process, enabling you to develop durable products.
Fatigue Analysis Software
The fe-safe suite provides:
- fe-safe: Accurate, reliable multiaxial fatigue analysis, regardless of the complexity of your loadings and model
- fe-safe/Rubber: Unique, leading-edge technology for the fatigue analysis of elastomers
- Verity Module in fe-safe: The original, patented Verity™ Structural Stress Method for seam, structural and spot-welded joints
- Smooth workflow between the SIMULIA portfolio of products: Abaqus, Isight and Tosca
- At a Glance
- Key Benefits
- Technical Highlights
fe-safe At a Glance
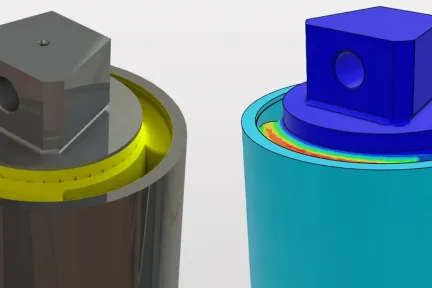
- Calculates fatigue lives at every point on a model, producing contour plots to reveal fatigue lives and crack sites without missing critical locations.
- Determines the intensity of stress change required to achieve a target design life. It highlights clearly where the component is under strength and opportunities to save material and weight.
- Estimates warranty claim curves based on probabilities of failure.
- Identifies which parts of a duty cycle are most damaging. In prototype testing, this could mean shorter tests with fewer actuators.
- Accounts for manufacturing effects such as residual stresses from a stamped or formed part, surface finishes, or the material variation effects in castings and forgings.
- Automatically detects triaxial stress states, e.g. due to contact, to use more extensive critical plane search
- Requires no special meshing, allowing for solid and shell elements in the same model.
- Offers fast random vibration fatigue analysis in the frequency domain via single-channel or multi-channel loading PSDs/CSDs with multi-axial critical plane analysis.
- Verity in fe-safe includes a unique calculation of the fatigue life of welded joints using the patented VerityTM Structural Stress Method. It can be used with multi-channel PSD/CSD loading.
- fe-safe/Rubber includes a unique technology for fatigue of elastomers using state of the art elastomer-specific algorithms.
- In addition, test signal processing functions and strain gauge fatigue algorithms are included in fe-safe standard.
fe-safe Key Benefits
With the fe-safe product suite as an integrated part of your design process, you can:
- Increase the fatigue life of safety-critical components.
- Optimize designs to reduce material usage.
- Reduce product recalls and warranty costs.
- Optimize and validate design and test programs.
- Improve correlation between test and analysis within a single user interface.
- Reduce prototype test times.
- Speed up analysis times, thereby reducing man-time hours.
- Increase confidence that product designs pass physical test schedules as "right-first-time."
- Reduce reliance on physical testing.
Fast
- Analyze assemblies of different parts, surface finishes and materials can be in a single run - fe-safe automatically changes the method of analysis as it moves from one material to another. Avail contour plots showing the fatigue life at each node, the factor of strength, and probabilities of survival to calculate in the same run.
- Highly efficient coding, native 64-bit code, and multi-threaded parallel processing allow fe-safe to analyze large finite element models and report results quickly. Parallel processing sees near linear speed increases.
Accurate
- Advanced multiaxial algorithms are the core of fe-safe.
- Unique nodal elimination methods ensure no trade-off between speed and accuracy.
- Users consistently report excellent correlation with test results. Continuous development ensures fe-safe maintains its position as the technology leader.
User-Friendly
- fe-safe has many default settings.
- fe-safe automatically selects the most appropriate algorithm based on the selected material.
- The option to save Standard analyses makes it ideal for the non-specialist fatigue analyst.
- Equivalent specifications in the materials database allow for the search of US, European, Japanese, and Chinese standards.
- Highly configurable for the advanced user.
- Drive direct interfaces to leading FEA suites such as Abaqus, ANSYS and Nastran (MSC, NX) from an intuitive, single-screen, Windows-based GUI.
fe-safe Technical Highlights
- Automatic hot-spot formation
- Critical distance – determining if cracks can propagate
- Damage per block
- fe-safe Custom Fatigue Algorithm
- Manufacturing effects
- Materials database
- Parallel processing
- Node-by-node property mapping
- Signal processing
- Structural optimization through integration with TOSCA
- Flexbody fatigue integration with SIMPACK
- Test program validation
- Virtual strain gauges
- Vibration Fatigue: modal dynamics, random vibration from load PSDs/CSDs, sine sweep
- Warranty curve
- Weld Fatigue
- FKM Guideline
Discover the Modules
Durability Analysis Software for Finite Element Models
Durability Analysis Software for Finite Element Models
Durability Analysis Software for Finite Element Models
Start Your Journey
Explore the technological advancements, innovative methodologies, and evolving industry demands that are reshaping the world of Durability Analysis and Finite Element Analysis. Stay a step ahead with SIMULIA. Discover fe-safe now.
FAQs About Fatigue Analysis
Structural fatigue analysis assesses material response within a structure when exposed to repeated loading over time. Structural fatigue analysis examines the structural integrity and how it changes under cyclic loading conditions. Analyzing factors like stress concentrations, load variations, and material properties, structural fatigue analysis can predict the lifespan of components and aid in preventing catastrophic failure due to fatigue damage.
Fatigue analysis is crucial in engineering to predict and enhance the lifespan of materials under cyclic loading. The following are the primary methods used in fatigue analysis:
- Stress-Life Method (S-N Curve): The S-N curve is a traditional method that involves plotting the material's stress amplitude against the number of cycles to failure. The S-N curve method is suitable for high-cycle fatigue analysis where the stresses are within the elastic range.
- Strain-Life Method (ε-N Curve): This approach is used for low-cycle fatigue analysis where the stress levels are high enough to cause plastic deformation. It involves plotting the strain amplitude against the number of cycles to failure.
- Fracture Mechanics Method: The fracture mechanics method is used to predict the growth of pre-existing cracks under cyclic loading. It's particularly useful for structures with crack-like defects and is based on principles from fracture mechanics.
- Fatigue Crack Growth Rate (da/dN vs. ΔK): This technique focuses on the rate at which an existing crack grows per loading cycle as a function of the stress intensity factor range (ΔK). It's crucial for predicting the remaining life of a cracked component.
- Multiaxial Fatigue Analysis: This approach is used when the stress state is complex, involving multiple directions. It requires more sophisticated models to predict failure, such as the critical plane approach.
- Energy Methods: These methods, such as the hysteresis energy approach, consider the energy absorbed in a material during cyclic loading as the primary driver for fatigue damage.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): FEA is a computational tool to predict stress, strain, and displacement of materials and structures under load. Combined with fatigue life models, it helps identify critical locations and estimate fatigue life. Each method has its specific applications, advantages, and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the type of material, the nature of the cyclic loading, and the available data.
fe-safe, a leader in fatigue analysis software for finite element models, interfaces directly with all major FEA suites and can meet the most demanding industry applications. It was the first commercially available software to focus on modern multiaxial strain-based fatigue methods. fe-safe is popular amongst designers for its accuracy, speed, comprehensive capabilities, and ease of use.
With fe-safe as an integral part of your design process, you can conduct fatigue analysis quickly and accurately. It fits smoothly into your design process, enabling you to develop durable, cost-efficient products. It also minimizes the risk of overlooking critical fatigue failure locations, reducing potential recall costs and warranty claims.
Cyclic loading is crucial in fatigue analysis. It involves repeated loading of a component, which can lead to high-stress regions and eventually cause crack initiation. Understanding cyclic loading patterns is important for accurate fatigue analysis.
Fatigue failure occurs in materials subjected to fluctuating stresses and strains over time, even if these stresses are below the material's ultimate tensile strength. Unlike abrupt failures due to a single application of high stress, fatigue failure develops gradually, stemming from the cumulative effect of cyclic loading.
Also Discover
Learn What SIMULIA Can Do for You
Speak with a SIMULIA expert to learn how our solutions enable seamless collaboration and sustainable innovation at organizations of every size.
Get Started
Courses and classes are available for students, academia, professionals and companies. Find the right SIMULIA training for you.
Get Help
Find information on software & hardware certification, software downloads, user documentation, support contact and services offering