Beijing Institute of Architectural Design
BIAD uses industry solution From Experience to Construction to set new benchmarks in smart hospital architecture, improving patient experience and processes with advanced design and simulation.
Envisioning a Smart Hospital of the Future
Situated along Beijing’s iconic Chang’an Avenue, a landmark hospital is undergoing a remarkable transformation to upgrade its facilities. Serving a vast and diverse population, the hospital is already renowned for its contributions to scientific research, disease prevention, and community health. This latest project involves a complete modernization, blending the character of its original 1950s architecture with cutting-edge technology and medical infrastructure, including advanced surgical wards, specialized treatment areas, and high-tech diagnostic facilities.
Harmonizing the old and the new is just one part of the challenge. The upgraded design must also optimize the hospital’s workflows and processes. Tackling this requires more than traditional approaches, it calls for innovative digital tools to manage the complexities of smart hospital design and operation.
Leading this ambitious renovation is the Beijing Institute of Architectural Design (BIAD). The Chinese architectural design firm has deployed Dassault Systèmes’ solutions to explore new methods in architectural design, construction, and operation, and break down siloes across disciplines. Its aim: to create a cohesive environment that benefits medical professionals, improves the patient experience, enhances operational efficiency, and delivers a future-proof and sustainable smart hospital for the years to come.
“Collaborating with Dassault Systèmes allows us to integrate advanced modeling and simulation technologies into our architectural designs, redefining how hospitals are designed, built, and operated in China’s new, sustainable era,” said Xu Quansheng, party secretary and chairman of BIAD. “Traditionally, hospital design focused solely on form and function. Now, with digital tools, we address the needs of doctors, patients, operators, and investors. Using process simulation and experiential modeling, we can develop comprehensive, integrated solutions before construction even begins.”
Modeling Hospital Processes and Safer Patient Experiences
At the heart of this transformation is a focus on optimizing patient experiences. Just as flight simulators are standard practice in aerospace design to ensure safety and functionality, similar virtual testing is being applied to this smart hospital renovation. By modeling and simulating every step of the patient’s journey during design, ranging from room layouts to hospital processes, BIAD’s team is able to identify potential issues early on and find the best solutions.
Every step of the patient journey is modeled to identify potential bottlenecks and inefficiencies, allowing designers to visualize and refine how patients navigate the hospital, from arrival through to treatment, recovery and discharge. From here, they can test how different configurations of operating rooms and patient wards affect the flow of both patients and staff, even considering how bed placement can support fast and smooth transfers to operating rooms or other functional areas.
“This approach transforms hospital design into more than just creating spaces and surroundings; it focuses on enhancing patients’ physical and emotional well-being during treatment,” said Huang Zhou, acting deputy director of the Eighth Engineering Institute at BIAD. “Every hospital has its own unique characteristics. The spatial design of a hospital revolves around its patients and the service workflows tailored to them. Artificial intelligence can classify patients and diagnostic processes within these workflows, using algorithms to optimize the medical service system. Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE platform opens up possibilities for generative AI in the future.”
“For doctors, the hospital must support a seamless workflow across clinical, surgical, and inpatient areas, allowing them to carry out their duties efficiently,” Xu added. “It should offer well-designed spaces for diagnosis, treatment, testing, laboratories, and wards that empower them to deliver exceptional care.”
The 3DEXPERIENCE platform is a powerful solution. It strengthens teamwork, connects upstream and downstream processes, ensures continuous information flow, and significantly improves productivity.
MODSIM Drives Effective Teamwork
Integrated modeling and simulation capabilities (also known as MODSIM) streamline the entire design process. Using CATIA, the powerful 3D parametric and generative modeling solution on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, designers can quickly create Building Information Models (BIM) in order to test and refine their ideas virtually, simplifying complex workflows and accelerating project timelines. At every stage, stakeholders from different disciplines work concurrently within the 3DEXPERIENCE platform and see the latest versions of the 3D models in real time.
“The model created during the design phase can be directly imported into the simulation module, enabling seamless transitions between the two with just one click,” said Feng Jing, smart hospital project manager of the Eighth Engineering Institute at BIAD. “Plus, any updates made in the design module are instantly reflected in the simulation. The 3DEXPERIENCE platform is a powerful solution. It strengthens teamwork, connects upstream and downstream processes, ensures continuous information flow, and significantly improves productivity.”
Designers must comply with industry standards for interior layouts and features. Over time, BIAD plans to build up a knowledge library of standardized designs. This includes wards, operating rooms, key equipment areas, and functional rooms such as CT and X-ray rooms, considering the specific medical equipment required in each space along with all manufacturer-provided information.
“After completing two or three similar projects, this knowledge base will cover 60% to 90% of common hospital scenarios,” said Liang Nan, deputy chief of the Information Department at BIAD. “For future projects, this approach will significantly improve efficiency, potentially cutting design time in half.”
MODSIM on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform guides BIAD’s design choices.
Simulating Airflow for Safety and Comfort
Environmental considerations are crucial in modern healthcare facilities, which require advanced systems for ventilation, airflow, and infection control. By simulating airflow patterns and the movement of pollutants throughout the facility using SIMULIA, BIAD’s design team can see where to strategically place surgical rooms and infectious disease wards to reduce the spread of contaminants.
“We simulated the internal airflow to understand how pollutants are diffused from wards, virtually testing different scenarios based on the position of walls, beds, and air inlets and outlets,” Liang said. “This supports us to design ventilation systems that rapidly expel pollutants, reducing the risk of cross-contamination and enhancing patient comfort and air quality.”
The simulations also address external factors such as weather and wind conditions. This helps to guide the layout of buildings to shield areas from high wind and make sure there is adequate ventilation in low-wind zones.
“Based on the results, we can strategically position infectious disease wards downwind to prevent contamination of other buildings,” Feng said.
By analyzing a room’s current conditions, we can predict energy needs in real time and adjust automated systems accordingly... This approach prioritizes occupant health while optimizing energy use, balancing safety, comfort, and sustainability.
Balancing Sustainability and Urban Complexity
The healthcare sector is under increasing pressure to reduce its environmental impact and boost cost effectiveness. By using SIMULIA’s advanced simulation tools to test energy usage, water management, and HVAC performance, the design team is able to highlight areas where improvements can be made. For instance, heat recovery systems can be used to reduce energy waste and improve energy efficiency. These insights will reduce the hospital’s carbon footprint but also deliver long-term savings in energy and maintenance costs.
“By analyzing a room’s current conditions, we can predict energy needs in real time and adjust automated systems accordingly,” Liang said. “On a clear day, fresh air can flow in naturally, reducing the need for ventilation. But if the air outside is polluted with smog, we can rely on internal air circulation. This approach prioritizes occupant health while optimizing energy use, balancing safety, comfort, and sustainability.”
The use of MODSIM tools is also crucial for managing the challenging logistics of working within an existing hospital site in an urban environment. The hospital’s central location in Beijing presents significant hurdles, such as limited space for construction. By simulating various scenarios, the design team can anticipate potential issues with access, traffic flow, and construction sequencing, helping to keep disruptions to a minimum and maintain smooth hospital operations throughout the renovation process.
“For example, by digitally mapping out the construction schedule alongside the hospital’s clinical workflows, the team can keep critical areas operational while construction continues in other parts of the hospital,” Huang said.
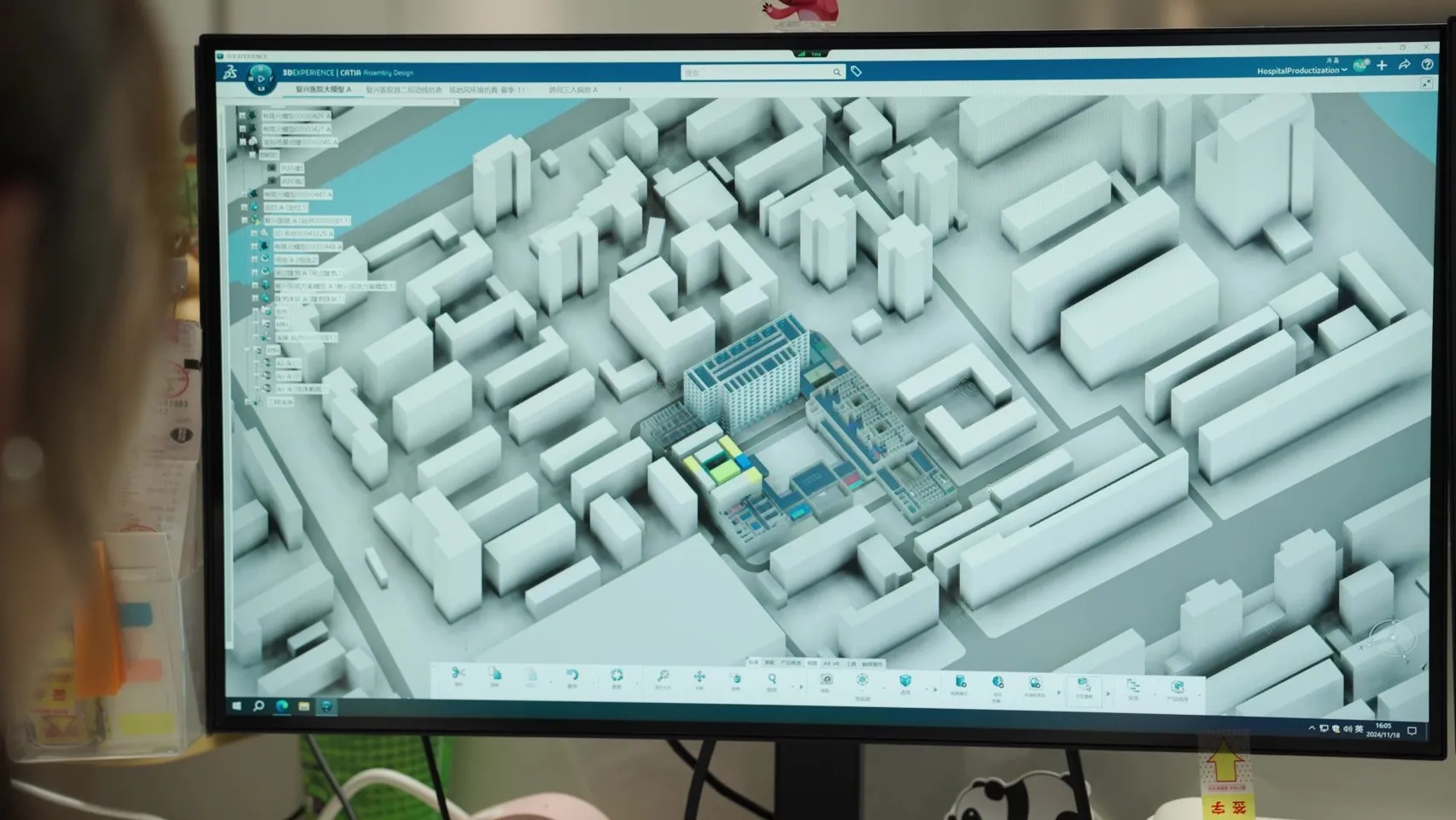
Forward Planning with Full Building Lifecycle Management
As the hospital evolves over time, incorporating new technologies and responding to future healthcare needs, it’s essential that the building’s design adapts. With Dassault Systèmes’ building information modeling and simulation capabilities, future expansions and room refits can be planned and tested virtually to make sure they integrate seamlessly with hospitals’ existing layouts. From construction through to operations and maintenance, the data collected and tested during the design phase will inform decision-making at every stage, enhancing the overall efficiency and longevity of the hospital.
“In this project, we addressed the challenge of balancing the long lifecycle of buildings (50+ years) with shorter cycles for equipment (five to 10 years) and rapidly evolving medical devices (such as pulse oximeters that are updated every one to two years),” Feng said. “The 3DEXPERIENCE platform integrates multidisciplinary data into a single platform, allowing us to visualize the impact of medical equipment on the overall design.”
The collaboration with Dassault Systèmes represents a major shift for us. It’s about more than designing buildings.
A Benchmark for Future Hospital Design
Innovations like this are a blueprint for the future of healthcare systems. BIAD hopes its integrated approach, supported by cutting-edge digital tools and sustainable practices, will set a new standard for smart hospital design and operational management.
“Our collaboration with Dassault Systèmes aims to streamline the entire workflow of hospital buildings, from design to construction and operation,” Liang said. “By creating standard, modular units, we’re accelerating the design process and defining the hospital’s function ahead of construction. It’s like working with a set of interlocking building blocks. Previously, we designed each piece individually. Now, by developing standardized blocks in various shapes and sizes, we can assemble them much more efficiently.”
This concept is known as productization. Turning architectural components into standardized, modular units will allow BIAD to create repeatable, scalable solutions that meet the complex demands of modern healthcare facilities while reducing design and construction timelines.
“Productization will become even more widespread as the future of our industry is driven by precision and led by intelligence,” Huang said.
Today, BIAD is positioning itself at the forefront of an industry where building performance and longevity is critical. The company’s vision now extends beyond design and construction to ensure that buildings continue to operate at peak performance throughout their lifespan.
“The Chinese government’s push to retrofit existing buildings aligns with these goals, blending old and new structures to meet carbon reduction targets and avoid unnecessary newbuild construction and demolition, both of which generate substantial carbon emissions,” Xu said. “The collaboration with Dassault Systèmes represents a major shift for us. It’s about more than designing buildings; it’s rethinking how they function, interact with their environment, and last for future generations.”

Focus on BIAD
Beijing Institute of Architectural Design is a large-scale state-owned architectural design and consulting institute established in 1949. The company specializes in engineering design, urban planning and design, engineering consulting, engineering cost consulting, tourism planning and design, landscape engineering design, and environmental engineering.
For more information: www.biad.com.cn



