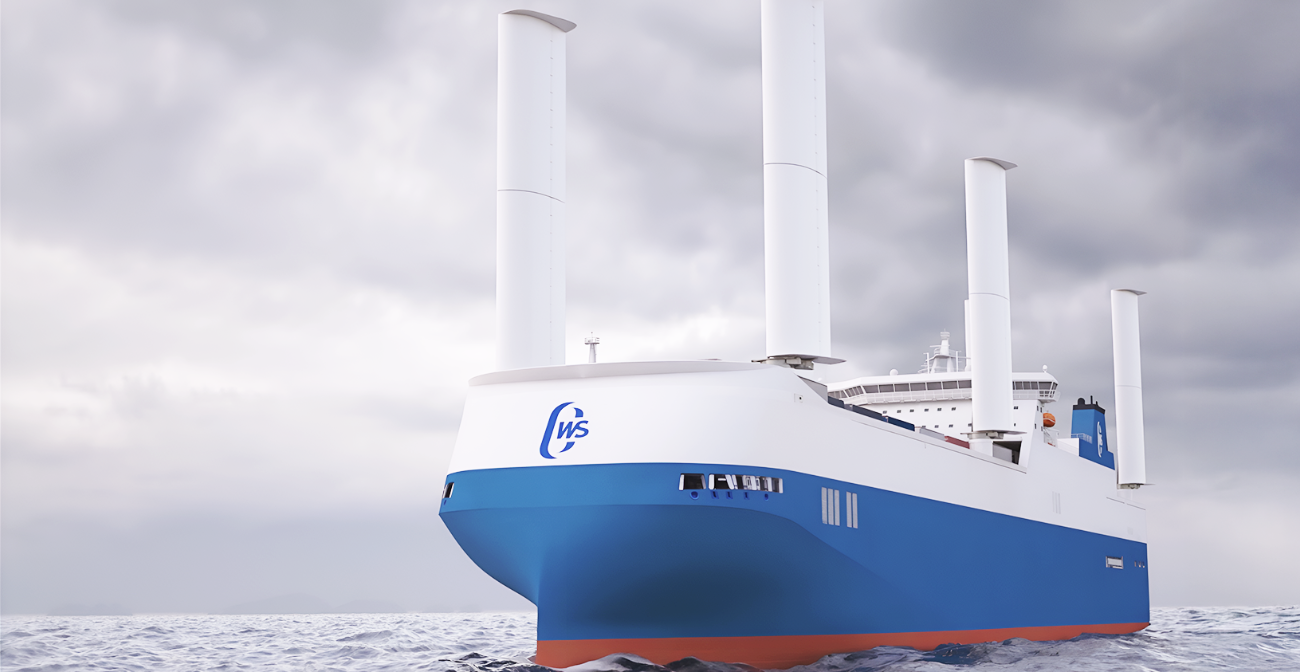
Computed Wing Sail
Computed Wing Sail (CWS) is charting a course for a greener future in maritime transport. Handling production from its factory in Saint-Nazaire, France, the company’s innovative wing sail technology is designed and virtually tested using the Designed for Sea industry solution experience. This approach enables CWS to continuously enhance the design of its wind-assisted propulsion system, balance durability and lightweight performance, and to speed up development.
The rise of wind-assisted propulsion at sea
A cargo ship cuts through the waves, its imposing steel hull gliding across the open waters to its destination. Rising high above its decks are rigid, foldable wing sails. When fully extended, they mimic the wings of a glider, generating lift that propels the ship forward, even in low wind conditions. Each sail’s asymmetric profile achieves a high lift-to-drag ratio while an advanced inversion system adjusts the angle according to the wind direction to deliver consistent power without compromising on speed or reliability. Fully automated, these sails require no manual hoisting and adjustment, making them easy to operate and placing no additional burden on the crew.
Behind this new generation of wind-assisted propulsion system is French engineering and industrial company Computed Wing Sail (CWS), which aims to tackle one of the maritime industry’s most pressing challenges: its heavy reliance on fossil fuels and resulting greenhouse gas emissions. CWS’s sail is designed to work alongside a ship’s engine and promises to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions substantially.
“Harnessing the power of a renewable energy source on the world’s busiest maritime routes is a logical step to helping the industry decarbonize,” said Agathe Caron, chief of staff at CWS. “The idea behind our wing sail is to use wind propulsion in a way that makes sense for modern shipping and will perform consistently in the real world, even on faster ships. We wanted to combine aeronautical principles with proven maritime technologies, creating a hybrid propulsion system that maximizes fuel savings without the need to replace engines.”
CWS’s wing sail innovation is more than a technical upgrade. It blends efficiency, sustainability, and futuristic design into a solution fit to address today’s environmental and economic challenges. In tests, CWS estimates its wing sails could achieve 30% to 50% in fuel savings onboard a ship. The company is using Dassault Systèmes suite of design and simulation solutions to make it all possible.
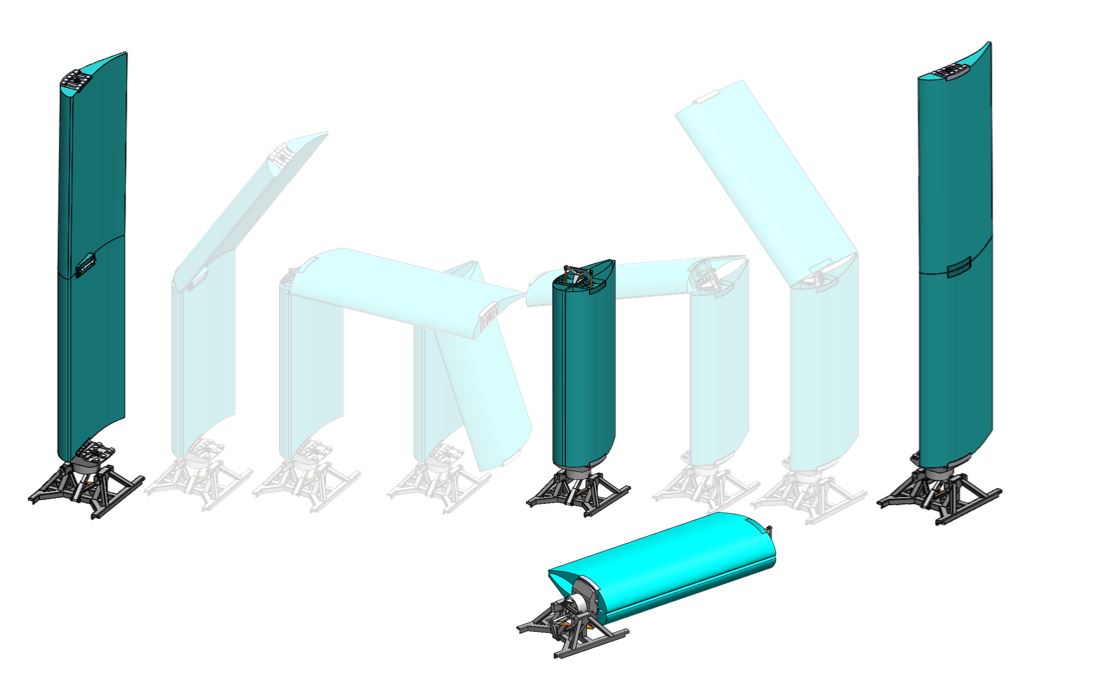
Continually optimizing the wind-assisted propulsion system
CWS has been busy refining its wing sail concept over the last 10 years. Its in-house engineering team has designed, engineered, and virtually and physically tested the propulsion system to continually improve its robustness and performance. The company uses Dassault Systèmes’ 3D design solution, SOLIDWORKS, to create detailed and accurate digital models of the wing sail including all components, from the wing itself to the mechanical systems that control its movement. Using SOLIDWORKS, engineers work on individual parts and see them within the context of the wider assembly.
“This approach allows everyone to focus on a specific part then easily share their progress with the rest of the team,” said Lucile Settineri, design engineer at CWS. “It’s also important for us to see how every component will fit and function in the final sail. For example, we have a hinge at the top of the wing sail and the 3D model showed us how much space we needed to account for the hydraulic system beneath the hinge.”
CWS’s engineers can also design and virtually test different shapes and try out various configurations and materials for the sail. This includes defining the framework for strength-bearing welded structures, such as the main frame. From here, they create detailed 3D models that can be sent to manufacturing suppliers for production.
“The wing sail has a metal frame, and we relied on SOLIDWORKS’ welded construction tools to design it,” Settineri said. “We can select from a library of standard structural shapes such as tubes and consider the most appropriate way to construct and join them together, making the process quicker and more efficient.”
CWS uses Dassault Systèmes’ solutions to handle product development, including SOLIDWORKS to design the wing sail and all components, and SIMULIA to simulate the loads and stress on the wing sail’s structure, striking the careful balance between weight and durability.
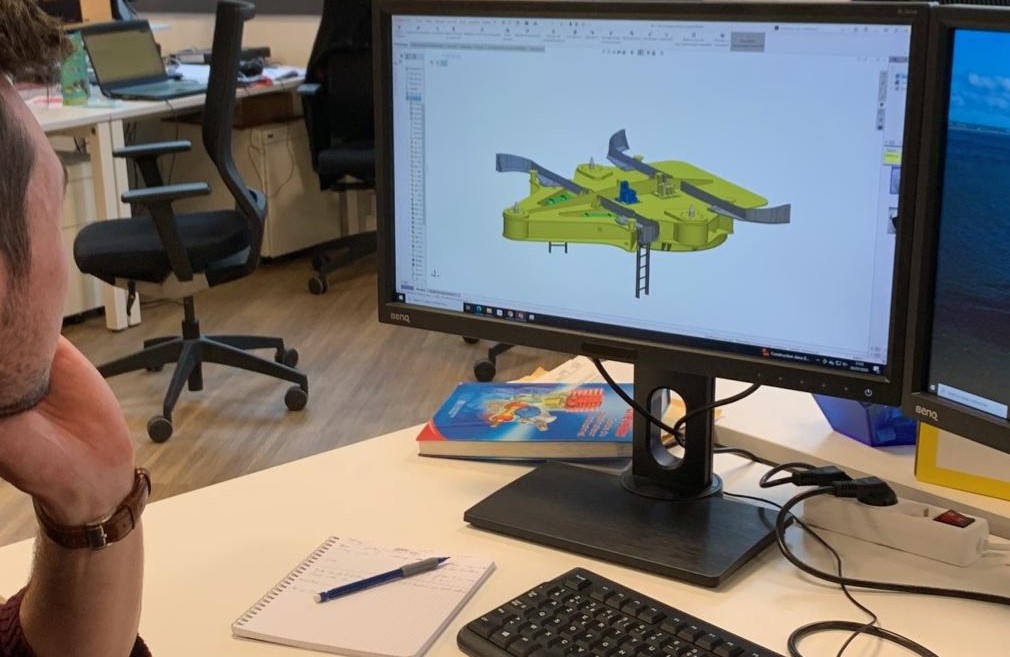

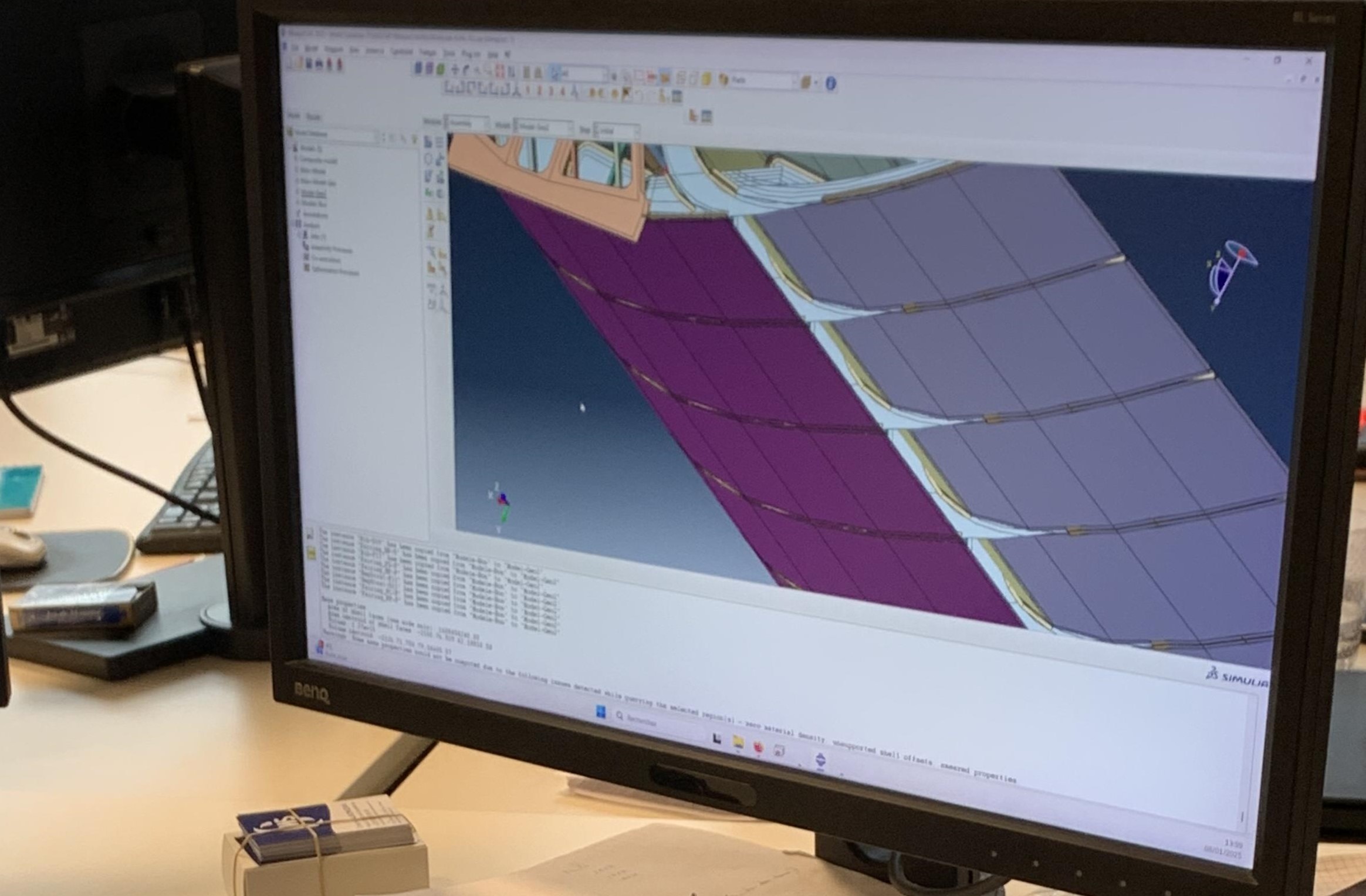
Improving durability at sea with simulations
CWS’s propulsion has been designed with versatility in mind. It’s suited for any type of vessel that would benefit from a hybrid propulsion system – from oil tankers to container ships – and can be installed on new ships or retrofitted on existing ones. This offers a cost-effective solution for operators aiming to reduce their carbon emissions and cut their fuel consumption. The sail’s lightweight design, compact footprint and folding mechanism means it takes up minimal deck space.
Achieving the perfect balance between lightweight design and durability is crucial. Every part undergoes rigorous virtual and physical testing to make sure it can withstand the harsh conditions of the open sea yet be as light as possible. With Dassault Systèmes simulation solution from SIMULIA, CWS can test the loads on both the main metal beam and the composite parts that form the shape of the wing. By reducing weight wherever feasible, CWS is able to enhance performance and efficiency. The testing also involves evaluating numerous points and interfaces between subsystems to make sure everything integrates seamlessly, and functions as intended.
“We thoroughly test each component to ensure the structure can withstand the expected loads,” said Nicolas Baldacci, composites engineer at CWS. “By analyzing stress data from simulations and comparing it to material properties, we can continually improve the model. Our goal is to create a structure that is both lightweight and strong enough to withstand the demands it will face at sea.”
Computed Wing Sail's advanced wind-assisted propulsion system blends efficiency, sustainability, and futuristic design into a solution fit to address today’s environmental and economic challenges.
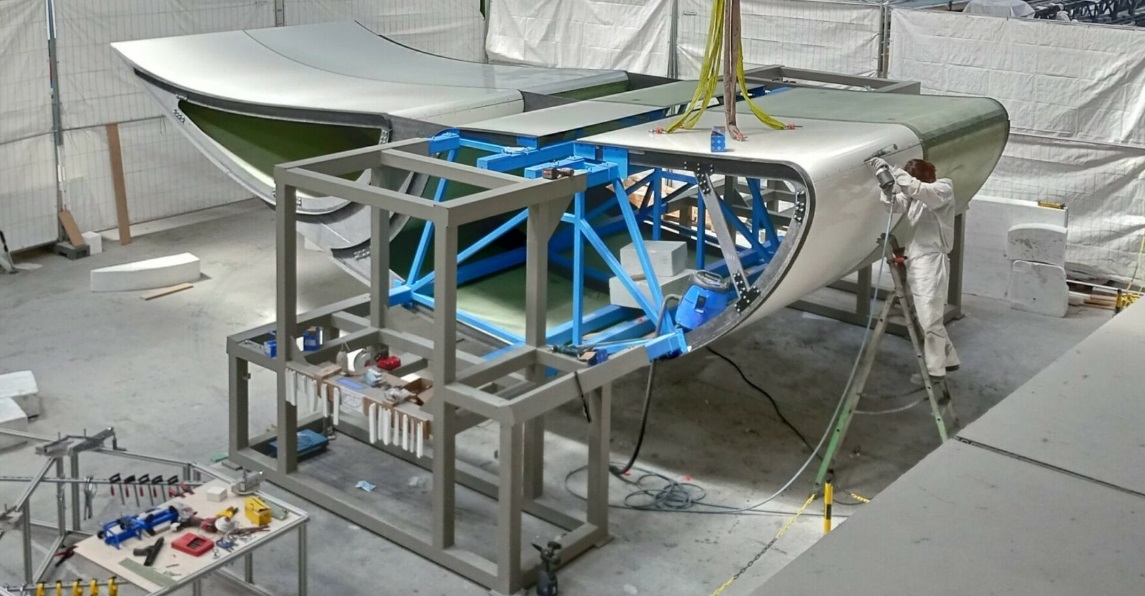
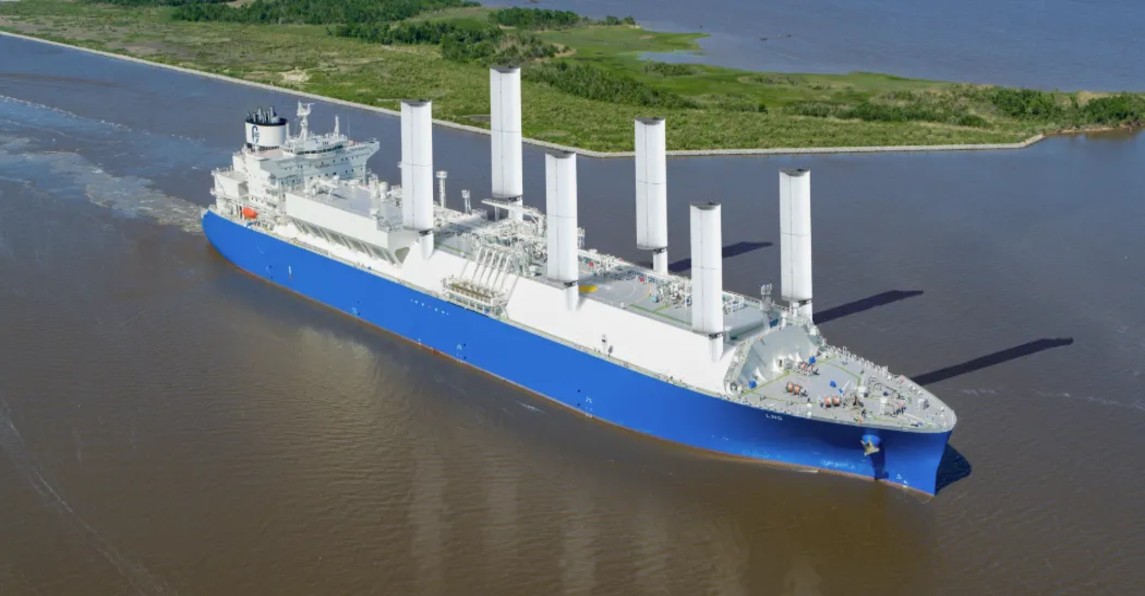


Becoming a key player in sustainable shipping
As CWS continues to push the boundaries of what’s possible with wind-assisted propulsion, it remains focused on enhancing its technological capabilities and expanding its reach within the industry. The company is now taking orders for delivery of its wing sail in 2026 and will soon finish its first full-scale, sea-worthy prototype. Until then, CWS will use its detailed 3D models to virtually showcase all the sail’s features, create compelling marketing assets, and engage potential customers.
Through research and strategic partnerships, the company is positioning itself as a key player in the maritime industry’s journey towards achieving net-zero. CWS’s technology partner, AvenAo, supports with the company’s ongoing digital transformation. This will be invaluable as it takes on new orders, scales up, and participates in groundbreaking industry initiatives such as the development of some of the first zero-emission containerships, featuring methanol-fueled engines and CWS wing sails.
“AvenAo has been invaluable for getting us up and running with Dassault Systèmes’ solutions and provides all the support we need,” Caron said. “They assisted with licensing and setting up our server cluster environment, which was critical. Looking ahead, we’re excited by the potential of the 3DEXPERIENCE® platform, and bringing all our design, simulation, engineering and manufacturing capabilities within a single environment so we can make data-driven decisions. We would certainly recommend Dassault Systèmes’ solutions to other businesses in the maritime sector.”
Discover more about the Designed for Sea industry solution experience.
FAQs

Focus on Computed Wing Sail
Computed Wing Sail (CWS) is the French company developing advanced wind-assisted propulsion technology. The company’s patented rigid foldable wing sail harnesses advanced aerodynamic principles and features a patented inversion system, allowing it to capture wind more effectively compared to traditional sails. By helping ships harness natural energy, CWS presents a sustainable and cost-effective solution for the maritime industry.
For more information: https://computedwingsail.com

Focus on AvenAo
AvenAo is an integrator of innovative industrial solutions, specializing in key areas such as design (CAD, simulation, PDM, documentation), production management and manufacturing. The company has established itself as one of the leading resellers of Dassault Systèmes solutions, including SOLIDWORKS and the 3DEXPERIENCE® platform.
For more information: https://www.avenao.com
