Beyond treatment: the shift toward prevention in life sciences and healthcare
Virtual twins are helping innovators across life science & healthcare organizationsfind new approaches that prioritize early intervention and improve comprehensivehealth management strategies to transform how the human body is understoodand treated.
In the VIRTUAL WORLD
we uncover the invisible and imagine new possibilities for understanding and caring for the human body...
...enhancing REAL LIFE
with groundbreaking medical devices and pharmaceuticals, shifting the Life Sciences & Healthcare industry’s focus to prevention over treatment.
Helping people live longer, healthier lives has always been the Life Sciences & Healthcare sector’s mission. Today, researchers are harnessing the potential of the virtual world to accelerate new horizons to understand the human body and develop a scalable approach to achieve precision medicine in the real world. By simulating complex biological processes, virtual environments allow medical professionals to delve deeper into how the body reacts in various scenarios, paving the way for targeted pharmaceuticals, innovative medical devices and safer, broader and more effective clinical trials. Harnessing the combined power of AI and data science, virtual worlds enhance understanding of the human body to lead to more accurate personalised medical diagnoses and tailored treatments. The integration of virtual technology in healthcare is not just a leap forward: it’s a revolution with tangible impacts for the real world in how we approach medical challenges and strive for better health for all.
Global healthcare systems turn to virtual twins to address challenges
Leveraging virtual twin experiences enables the transformation of globally overstretched healthcare systems, delivering on the promise of new virtualization and data opportunities to address myriad challenges faced by the healthcare industry.
The global healthcare industry has reached a tipping point. Overwhelmed by the complexities of diverse regulations, aging populations and increasing demands for more precise personalized treatments, it has become financially unsustainable. Others offer band-aid AI solutions that simply mask the problems. Dassault Systèmes takes a different approach, explained in our white paper Virtual Twin Experiences in Healthcare: Next Generation Precision Medicine. Here, we outline a systematic transformation from today’s massively fragmented,data-driven systems to scalable, knowledge-based virtual twin experiences as the optimal way to meet healthcare’s challenges.
Key points
1. Virtual twins help navigate massive data complexity by integrating science with machine learning and AI to analyze vast data sets, identify key relationships and automate routine tasks. This enhances decision-making, reduces human error and improves patient outcomes.
2. The use of virtual twins can offer:
Patient experiences that offer a detailed, dynamic representation of the human body and individual health conditions. By integrating data from biosciences, material sciences and information sciences, virtual twins provide a comprehensive understanding of human anatomy and physiology, enabling precise diagnostics and patient-centric, personalized treatment planning.
Hospital structure and operations optimized by simulating design, layout and operating conditions as well as staff and patient workflows. Improvements to the entire patient journey can be envisioned and changes to overall operational efficiency can be safely evaluated.
Entire healthcare systems represented at a functional level. Policymakers can visualise critical processes such as resource allocation, public health strategy optimization and evidence-based policymaking.
3. The 3DEXPERIENCE and MEDIDATA platforms provide secure foundations for healthcare solutions powered by virtual twin experiences. Real-world data can be used to simulate patient populations, systemic treatment effects and long-term outcomes. Researchers can perform complete in silico clinical trials or construct synthetic control arms that not only accelerate the development of new innovations but also reduce the uncertainty and scale of physical trials, improve success rates and lower overall costs.
Future outlook
Virtual twin experiences will redefine healthcare practices as they have transformed all other industries that have successfully navigated digital transformations.
Patient-centric, multidisciplinary care is enabled, while enhanced diagnostic and treatment accuracy translates to operational efficiency gains. Generative machine learning methods combine proven multi-scale/multiphysics simulation of complex systems with curated databases of patient experience to create trustworthy medical processes that are scalable and efficient, ensuring better patient journeys and outcomes. Healthcare becomes more predictive, preventive and patient-enabled.
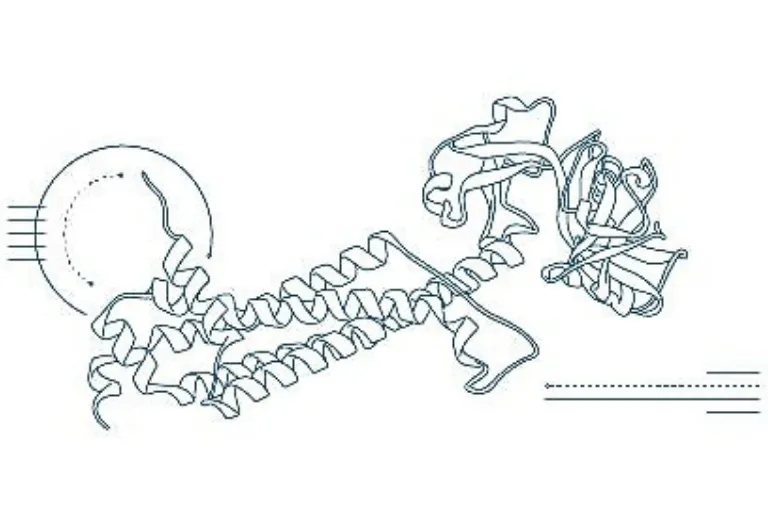
Uncovering the mysteries of protein folding
As a member of the OpenFold consortium, Dassault Systèmes is working with other biotechnology leaders to accelerate AI-powered research and development, helping scientists, researchers and bioengineers to discover new drugs and better understand disease. The following text is an excerpt from a February 2024 blog post by Tien Luu, PhD Senior Portfolio Manager and Principal Scientific Specialist within Dassault Systèmes’ BIOVIA.
Exciting and inspiring – those are the best words to describe the OpenFold consortium meetings and discussions. In the drug discovery world, AlphaFold2 is now almost synonymous with solving one of the most elusive problems in computational biology and chemistry: protein folding. AlphaFold2, as the name implies, is built upon its predecessor AlphaFold’s success at the 2021 14th Critical Assessment of Structure Prediction (CASP14) where it trounced the competition by accurately predicting the unknown structures of proteins from their amino acid sequence.
In 2024, Demis Hassabis and John Jumper of Google DeepMind were among the Nobel Prize laureates in Chemistry, honored for developing AlphaFold2 – an AI system that uses a deep neural network architecture trained on an extensive dataset of known protein structures to predict complex folding patterns with remarkable accuracy. DeepMind has published the comprehensive details of AlphaFold’s methodology and findings, making its cutting-edge algorithms publicly available. But that move may be seen in a different light when you learn about OpenFold.
AI for all: OpenFold’s role in drug discovery
OpenFold was founded in February 2022 by the AlQuraishi lab at Columbia University, Arzeda, Cyrus Biotechnology, Outpace Bio and Genentech’s Prescient Design. OpenFold is modelled after pre-competitive technology industry consortia, embodying the ethos of open science, encouraging transparency, sharing knowledge and accelerating scientific breakthroughs. Its first release in June 2022 included not just the inference code and model parameters reproducing and improving upon AlphaFold2’s speed and accuracy, but also the full training code that could allow a full set of derivative models to be trained for specialized uses in drug discovery of biologics, small molecules and other modalities.
As stated on its web pages, OpenFold “is a non-profit AI research and development consortium developing free and open-source software tools for biology and drug discovery.” It aims to democratize the power of biological AI and lead a community-driven effort to make advanced protein structure prediction tools available to researchers and scientists in academia, biotech and pharmaceutical companies across the globe. Without a doubt, its inception played a part in encouraging DeepMind to share the details of their discovery and has ushered in an exciting new era of transparent and collaborative research. DeepMind has continued their development of AlphaFold models. In May 2024, they released AlphaFold3, expanding beyond protein structure prediction to model complexes involving DNA, RNA, ligands, and more with significantly improved accuracy.
AlphaFold3 may help crack long-standing challenges such as accurately predicting protein-ligand structures and potentially replacing current industry-standard docking methods. This work was done with Isomorphic Labs, a commercial venture stemming from the original AlphaFold DeepMind team, who are reimagining the “entire drug discovery process from first principles with an AI-first approach.” Since then, OpenFold has been working towards replicating AlphaFold 3’s capabilities – such as modeling interactions involving proteins, DNA, RNA and small molecules – using publicly available data. Recently, it was announced that it will be fine-tuned using proprietary data from biopharma leaders AbbVie and Johnson & Johnson in a confidentiality-preserving and secure federated environment powered by Apheris. OpenFold3 is expected to be released in the spring of 2025 and hopefully incentivise the continued sharing of knowledge to promote advancements in bioinformatics, drug discovery and structural biology that wouldn’t be imaginable five years ago.
Embracing a New Era: OpenFold’s journey to the 3DEXPERIENCE platform
Dassault Systèmes, through its BIOVIA brand, became an industry consortium member of OpenFold in November 2022. Our impetus is to deliver valuable software solutions with the best methodologies for pharmaceutical and agricultural product design, helping our users solve real-world problems in drug discovery, disease understanding and bioengineering. We are now enriching our drug design experiences by amplifying the power of long-established and validated physics-based modeling and simulation methods with cutting-edge AI methods. In February 2024, the OpenFold (monomer) and the AlphaFold (multimer) models were made available to BIOVIA Discovery Studio Simulation users on the 3DEXPERIENCE platform as an alternative to the traditional homology modeling algorithm MODELER. Subsequent advances later in 2024 incorporated other Nobel-Prize winning AI models for generative biologics design, allowing our users to combine the power of AI with traditional molecular modeling and simulation for complete drug discovery workflows.
BIOVIA empowers science-driven innovators to accelerate breakthroughs from research to commercialization. We do this by unifying in-silico and wet-lab experimentation across biology, chemistry, and materials science through virtual twin experiences, generative AI, and standardized data and processes on a common platform. With OpenFold Consortium and our other partners, we bring cutting-edge science into our open ecosystem, helping researchers design and develop novel therapies faster.
MEDIDATA launches new solutions to speed oncology and vaccine trials
New offerings combine technologies and learnings from thousands of previous trials to streamline study management for Phase II and Phase III studies, reinforcing FDA guidance for patient-centered study design and execution.
In October 2024, MEDIDATA introduced two new bundled offerings to meet the growing demands of oncology and vaccine research. MEDIDATA Oncology Solutions and MEDIDATA Vaccine Solutions reinforce the US Food & Drug Administration’s guidance for patient-centred endpoints, adaptive trial designs and trial diversity. By unifying key trial components such as real-time patient-reported outcomes and imaging management, these bundled solutions willaid sponsors by reducing trial complexity, accelerating decision-making and improving assessments of treatment efficacy and safety.
“Oncology and vaccine trials face significant challenges in recruiting diverse patients, ensuring rapid execution and maintaining and monitoring patient safety,” said Joseph Schmidt, chief operating officer, MEDIDATA.
“By making these new bundled capabilities readily available to customers, we can deliver a solution built on MEDIDATA’s vast experience and expertise in these two important therapeutic areas. These bundles are designed to help customers navigate the complicated stages of these studies while advancing life-saving treatments.”
With more than 25 years of oncology and vaccine experience and the largest global trial datasets, MEDIDATA has managed approximately 9,000 oncology studies and 750 trials in vaccines. In 2024, it was recorded that 86% of oncology drug approvals went through MEDIDATA. The brand was also on the frontlines of COVID-19, supporting hundreds of trials, including the development of the one of the most effective MRNA vaccines used to fight the virus.
Advancing radiology through artificial intelligence for better patient care
At the 10th International Virtual Human Twin Experience Symposium, Professor Laure Fournier, an expert radiologist at Assistance Publique – Hôpitaux de Paris and Université Paris Cité, shared insights into the groundbreaking integration of AI in imaging workflows.
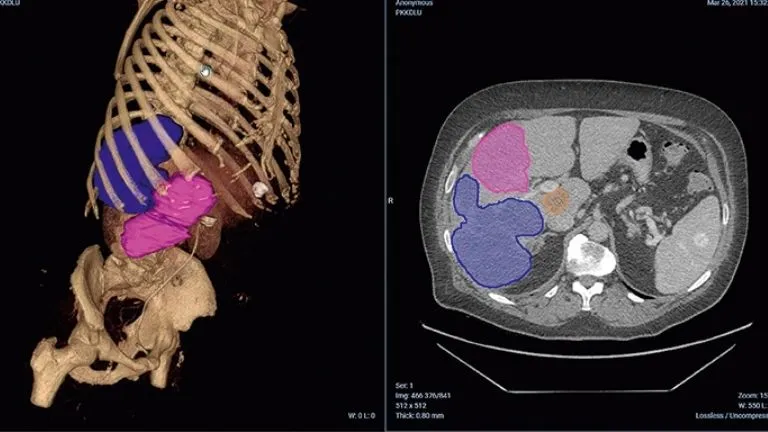
The Twinonco project funded by the French government as part of France 2030 and spearheaded by Professor Laure Fournier’s institution and Dassault Systèmes focuses on two primary goals: enhancing reproducibility and saving time for medical experts. Professor Fournier explained how innovative AI-driven tools are expected to reshape traditional workflows by automating and standardizing key processes. A powerful example is the use of AI to detect and delineate metastatic lesions on medical images, transforming 2D slices into comprehensive 3D visualizations. These 3D models may provide detailed insights into disease progression, offering data that manual analysis often cannot match.
The integration of AI addresses critical challenges faced by radiologists, such as processing vast volumes of imaging data. For instance, analyzing stacks of hundreds of CT slices to identify andassess lesions is time-intensive and prone to variability. AI-powered tools can streamline this by automatically identifying lesions across multiple slices, consolidating them into 3D entities then translating the findings into actionable reports. This improvement should save time and enable the team to focus on higher-value tasks, such as personalized patient communication.
Professor Fournier noted three illustrative case studies to emphasize how AI tools can improveclinical decision-making. First, in cases of mixed responses to immunotherapy, where both response and stability of lesions are observed, AI can aid in defining global patient benefit and potential treatment success. Second, AI can help detect subtle oligoprogressions, where a small number of lesions progress against a backdrop of general improvement. Such precision is crucial to targeting these anomalies early as they may be treated locally. Lastly, with complex disease presentations involving multiple progressing lesions across organs, AI can provide a quantifiable overview of tumor burden, vital for evaluating treatment effectiveness. Looking ahead, Professor Fournier discussed evolutionary changes that AI could bring to cancer care. A data-driven global view of a patient’s disease will enable monitoring of disease progress more precisely, moving beyond subjective assessments. AI tools will foster a shift from population-based treatment decisions to strategies tailored to the unique characteristics of patients. By analyzing historical data and outcomes from similar cases, clinicians can customize care to complex, atypical responses.
Snapshots of Innovation
- Clinical Trial Project
- Clinical Data Studio
- Rave Lite
- Generative AI
- Advance cancer research
- Neurological trials
- Patient Payments
- Hands-On Medical Learning
In Silico Clinical Trial Project
In 2019, the US FDA and Dassault Systèmes launched the in silico Clinical Trial Enrichment Project to explore the potential for virtual twins of patients to evaluate safety and effectiveness of new medical devices. Upon project completion in 2024, the group published a detailed Playbook for the industry to follow on regulatory use of in silico Clinical Trials. This guide enables exploration of the game-changing potential of in silico clinical trials in regulatory processes.
MEDIDATA’s Clinical Data Studio
MEDIDATA’s Clinical Data Studio is a unified experience that unlocks the true power of clinical research data. This groundbreaking technology gives stakeholders greater control over the quality of data and the ability to deliver safer trials to patients faster.
MEDIDATA Rave Lite: Supporting growth in early-and-late stage clinical trials
MEDIDATA Rave Lite is an extension of MEDIDATA’s gold-standard clinical research software, MEDIDATA Rave EDC, but is designed explicitly for Phase I and Phase IV studies. Regardless of company size, therapeutic focus or pipeline, Rave Lite provides efficient electronic clinical data capture (EDC), management and analysis solutions with a tailored pricing model.
Challenges and opportunities in implementing generative AI
Generative AI is still in its early stages of adoption, but its potential impact on the Life Sciences& Healthcare sector is undeniable. As generative AI matures, its role in revolutionizing clinical research and healthcare will only grow. The organizations that proactively navigate its complexities today will be best positioned to lead tomorrow.
Clinical trials to advance cancer research
A 15-year relationship between MEDIDATA and the US National Cancer Institute (NCI), part of the National Institutes of Health, has been extended. This renewed commitment for an additional five years consolidates their joint efforts and underscores their mutual dedication to advancing cancer research
Transforming neurological trials
Neuroscience solutions leader Cogstate has entered into a partnership with MEDIDATA to reshape clinical trials and outcome measurement for central nervous system (CNS) diseases across neurodegenerative, psychiatric, motor and rare neurodevelopmental disorders. This relationship will deliver higher-quality data collection with increased efficiency and accuracy.
Clinical research Patient Payments
MEDIDATA Patient Payments streamlines trial-related stipends and reimbursements for clinical research patients. Automating the payment lifecycle addresses the long-standing challenge of compensating participants for their time, effort and study-related expenses, while solving for growing concerns around the financial toxicity of clinical trial encounters.
Project-based approaches to learning
Trier University of Applied Sciences students created a 3D-printed model for Barmherzige Brüder Hospital medical students and junior residents to practice manual surgical procedures, including cranioto-mies, burr holes, biopsies and computer-assisted techniques.