Designing the Future of Shipping: Wind-Assisted Ship Propulsion
Succeed with WASP retrofitting strategies using unified modeling & simulation
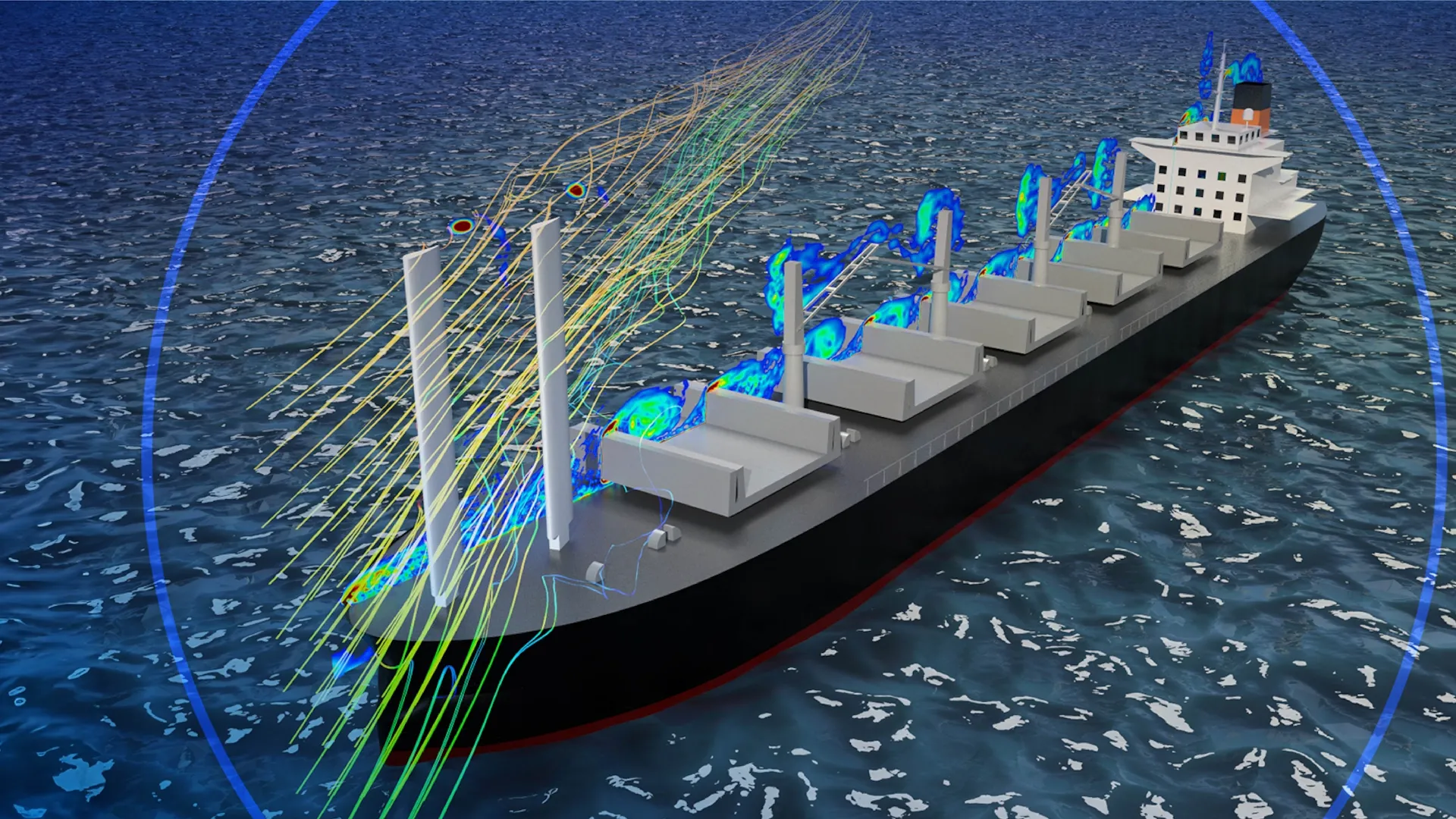
Wind-assisted ship propulsion (WASP) is transforming the marine and offshore industry by offering a sustainable path to reduced fuel consumption and emissions. As shipping faces increasing pressure to decarbonize, WASP technologies—such as sails and airfoils—provide a practical solution for both new builds and retrofits.
However, integrating WASP systems presents unique engineering challenges, from aerodynamic optimization and structural integrity to system integration and regulatory compliance. Unified modeling and simulation (MODSIM) empowers engineers to address these complexities, enabling rapid design iterations, virtual testing, and performance optimization before costly prototyping. By leveraging advanced simulation tools, marine innovators can accelerate WASP adoption, minimize risk, and drive sustainable progress across the shipping sector.
Designing the Future of Shipping: Wind-Assisted Ship Propulsion
Optimizing WASP Component Design with Simulation
The design of wind-assisted ship propulsion (WASP) systems begins with optimizing the sail or airfoil shape for maximum efficiency. Using advanced simulation tools, engineers can refine 2D airfoil outlines and transform them into 3D models, enabling rapid testing and adjustment. This unified modeling and simulation (MODSIM) approach allows for quick evaluation of aerodynamic performance, structural integrity, and motion, ensuring the WASP components are lightweight, robust, and tailored to real-world operating conditions—accelerating innovation and reducing development risks.
What are the key challenges for integrating Wind-Assisted Ship Propulsion [WASP] systems on a ship?
Optimal Sail Placement
Avoiding airflow disruption from ship structures to maximize WASP efficiency and ensure crew safety.
Bridge Visibility and Navigation Lights
Preventing sails from blocking bridge sightlines and navigation lights to maintain safe operations.
Antenna Interference and Radar Blind Sectors
Minimizing signal disruption and radar blind spots caused by WASP sails and structures.
Lightning Strike and Electromagnetic Effects
Protecting ships from lightning strikes and electromagnetic interference introduced by tall WASP sails.
"By analyzing stress data from simulations and comparing it to material properties, we can continually improve the model.”
Computed Wing Sail: CWS
CWS is charting a course for a greener future in maritime transport. Handling production from its factory in Saint-Nazaire, France, the company’s innovative wing sail technology is designed and virtually tested using Dassault Systèmes solutions.
Accelerate Sustainable Shipping with Dassault Systèmes MODSIM
Wind-assisted ship propulsion (WASP) offers a powerful route to greener, more efficient shipping, but success depends on overcoming complex engineering challenges. Unified modeling and simulation (MODSIM) brings together design and analysis in a single collaborative environment, enabling faster development, reduced costs, and minimized risks. With Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE platform and SIMULIA simulation tools, marine engineers can optimize every stage of WASP integration—from concept to certification. Discover how our solutions empower you to lead the way in sustainable maritime transformation and achieve your decarbonization goals.