Digital and Sustainable – The next milestone in shipbuilding transformation
Driven by intense competition and the compelling sustainability imperative, shipbuilding is currently being developed through transformative approaches.
Some of the main principles of shipbuilding were adopted back in the 17th century. However, driven by intense competition and the compelling sustainability imperative, a wave of innovation is currently carrying the industry to develop transformative approaches.
NAVAIS: setting the course for next-generation European shipbuilding
Building on Damen’s proven standardization experience, one of its divisions, Damen Shipyards Gorinchem, is coordinating the New Advanced Value Added Innovative Ships (NAVAIS) program in close cooperation with Netherlands Maritime Technology (NMT), Dassault Systèmes, Bureau Veritas, Delft University of Technology, MARIN (The Maritime Research Institute Netherlands) and 10 other partners.
Co-funded by Horizon 2020, the biggest EU Research and Innovation program ever conceived, NAVAIS aims at finding new shipbuilding methods to maintain the European shipbuilding industry’s global leadership in complex vessels, while also making sustainability more integral to new projects, from the design stage onward.
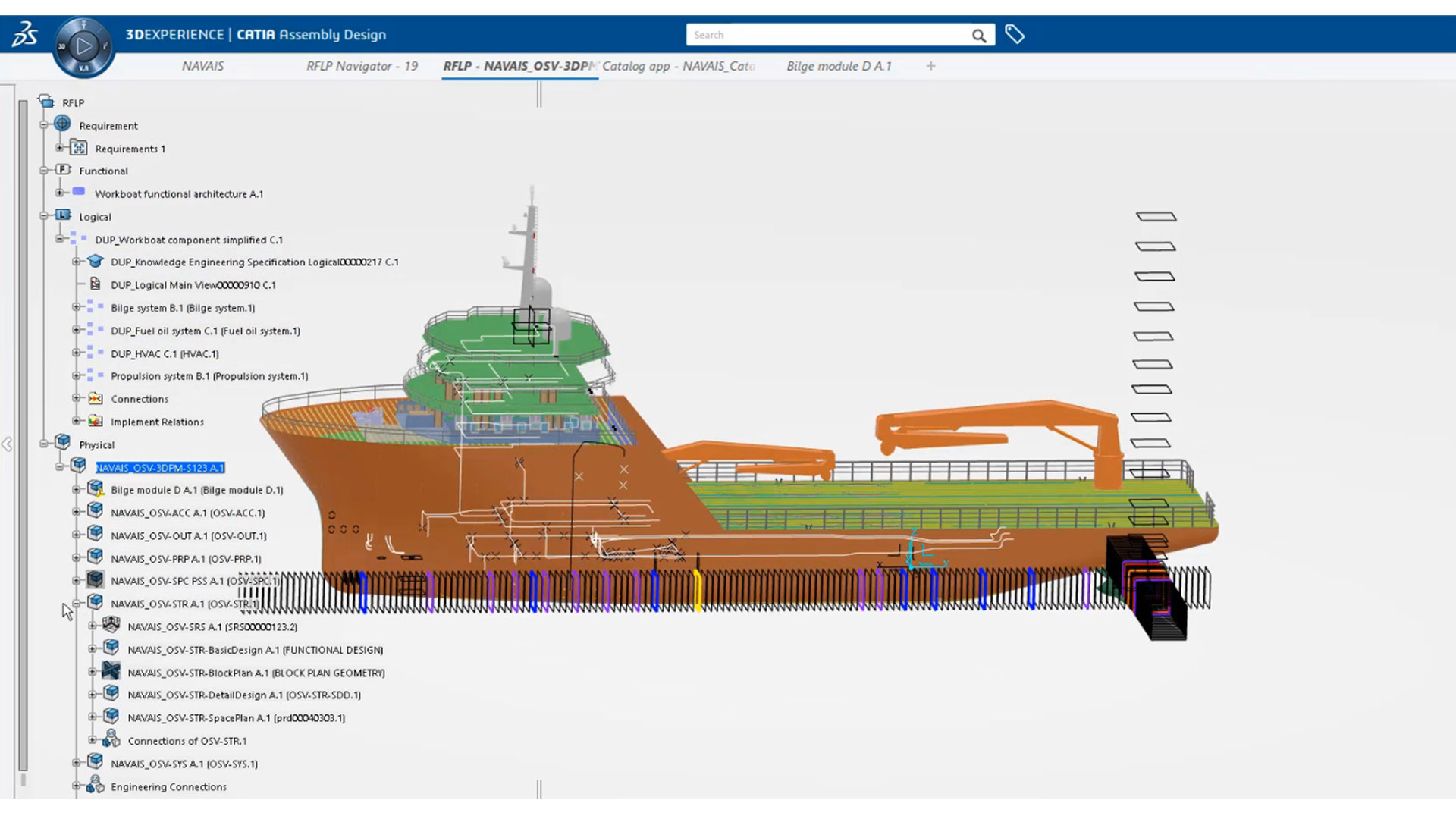
NAVAIS is developing guidelines and KPIs for low-impact ship design and operations, reducing or, preferably, eliminating emissions (exhaust emissions, oil, ballast water, as well as airborne and underwater radiated noise) to the environment. To increase efficiency in vessel design and flexibility in production networks, NAVAIS explores standard and modular design and production principles. Leveraging a Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) approach, NAVAIS is developing a platform-based modular product family supported by the 3DEXPERIENCE platform, focusing specifically on e-ferries and workboats.
The program will profoundly change the way in which new shipbuilding projects are approached. Traditionally, these projects involve an engineering-to-order business model, where specifications are defined and design work is carried out on the basis of the customer’s needs and vessel's intended purpose. The new approach involves an assemble-to-order business model, resulting in shorter lead times, consistent quality, reduced design and production costs and improved supply chain integration, while ensuring the continued focus on clients’ specific needs.
To achieve this, users define related groups of products that share characteristics, components, subsystems, interfaces and manufacturing processes; these groups meet a wide array of customer requirements, and various modules are created with the required attributes to fulfill the various functions of a vessel’s structure.
It also involves defining the modular design process and the library of modules that can be reused: design and production data, business rules, documents and spatial information are stored in the library, allowing users to standardize production and propose multi-user environments to create models, test behavior and centralize information using a MBSE approach.
NAVAIS is defining a completely new class-approval procedure, where pre-engineered product modules are approved to support an evolution to an assemble-to-order business model. Bureau Veritas also simulates the vessel’s energy efficiency within the 3DEXPERIENCE platform.
The manufacturing plan can be simulated for each production module, and the process plans for various modules can be combined to create the main process plan for the vessel as a whole. NAVAIS is scheduled to complete its work in June 2022 and demonstrate the feasibility of these concepts for shipbuilding.
The MBSE approach decoded
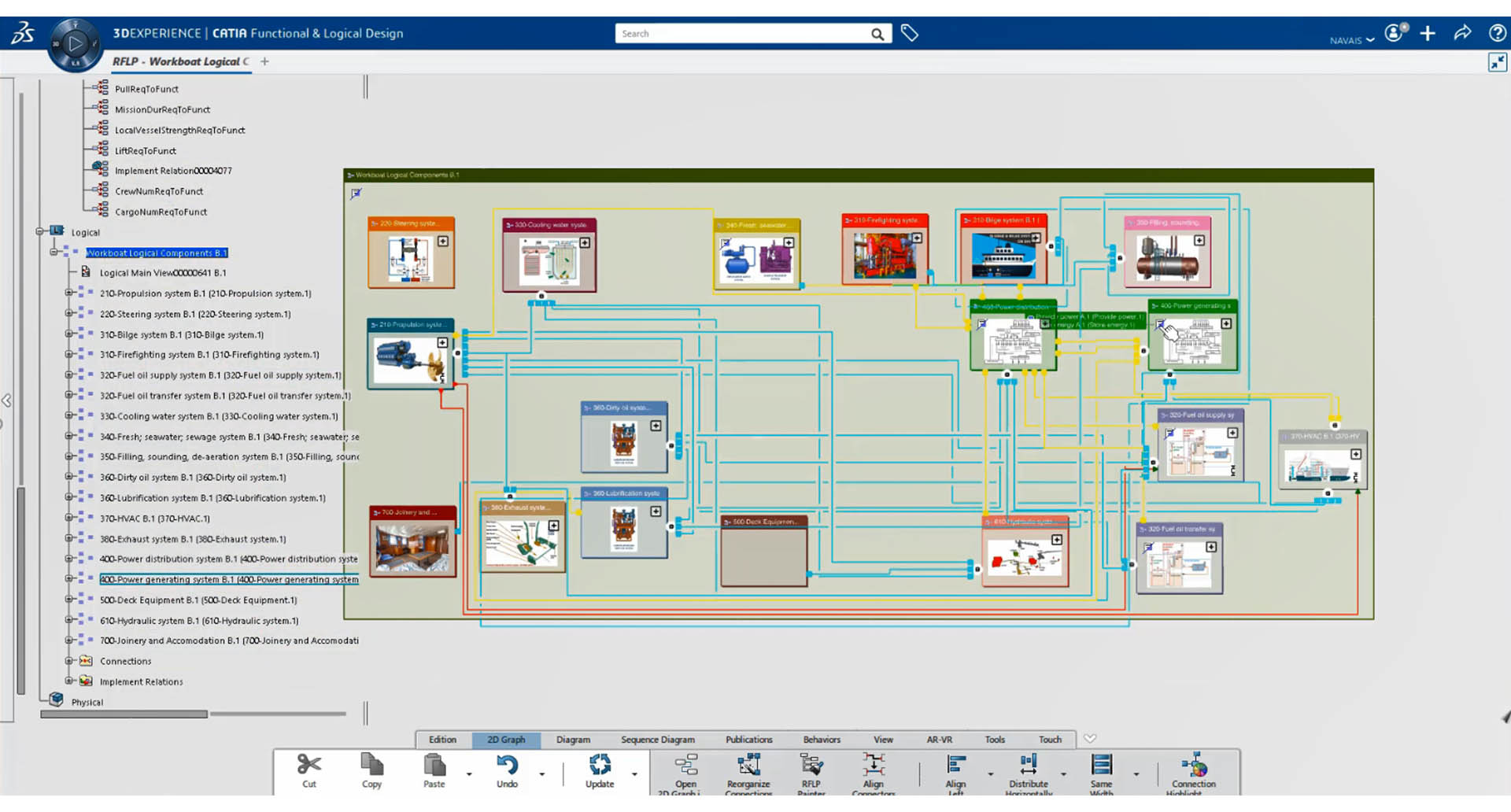
Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) is inseparable from the ever-growing sophistication of products across industries. The Marine & Offshore industry is no exception. Marine assets are complex systems that involve multi-disciplinary teams dealing with mechanics, electronics, software, telecommunication, cybersystems, chemicals, batteries, hydro-dynamics and more.
Consequently, MBSE methodology, which focuses on creating and using multi-physics 3D as the primary means of exchanging information between engineers, as opposed to documents, is being gradually adopted across the naval and commercial shipbuilding segments to cut through the complexity.
A paperless shipyard, thanks to virtual twin technology
CSSC Jiangnan Shipyard, one of China’s largest shipbuilding companies, builds, repairs and converts commercial ships. Founded in 1865, it has a solid reputation in complex vessels. After decades of development, the company wanted to strengthen its competitiveness, focusing on higher-value vessels that include gas carriers, large container ships and scientific vessels and moving away from volume production of low-value ships such as bulk carriers. In 2015, Jiangnan Shipyard selected the 3DEXPERIENCE platform to lead the digital transformation of the CSSC Group and take China’s shipbuilding industry to the next technological level.
The transformation meant moving from a traditional shipyard organization based on 2D documents and plans to a paperless shipyard, putting the 3D model at the center of its design and production processes. To ensure digital continuity and have a solution based on 3D models that factor in all of its processes end-to-end, Dassault Systèmes helped Jiangnan Shipyard to define, share and monitor key performance indicators based on typical use cases.
The first vessel ever designed and built using this 3D model-based approach is the Haixun 160. Jiangnan Shipyard did not use a single piece of paper for its design or construction, which required only three months for the engineers and workers to build the various parts of the ship and assemble them. On site, teams no longer have to look at often-complex 2D blueprints. Each detail of the ship can be closely examined directly on the 3D model, and a laptop or a tablet is all that is required to access all of the detailed information.
Some of the key benefits include:
- Avoiding error-prone interpretation during manufacturing, thanks to direct usage of 3D, which provides a perfect match between the real and virtual world, with a reliable end-to-end digital thread.
- Using Virtual Twin technology with VR and ergonomics, the 3DEXPERIENCE platform can simulate on-board crew actions such as walking, operations, and maintenance. This helped the shipyard to detect issues early in the design phase, effectively control and manage construction cost, shorten cycle time, and improve build quality.
- Using 3D models instead of drawings led to a reduction of errors, thanks to better understanding.
Jiangnan Shipyard plans to further advance its processes, leveraging the virtual twin to help ship owners with maintenance throughout the ship’s lifecycle